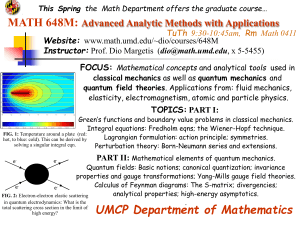
CH160: Professor Peter Sadler Introduction to inorganic chemistry
... scattered back toward the source. - Rutherford concluded that atoms contain a verysmall (compared with size of the atom) positive charge, which can repel alpha particles if comes close enough 1911 Rutherford model of atom Electrons move in circular orbits around positively-charged nucleus - classica ...
... scattered back toward the source. - Rutherford concluded that atoms contain a verysmall (compared with size of the atom) positive charge, which can repel alpha particles if comes close enough 1911 Rutherford model of atom Electrons move in circular orbits around positively-charged nucleus - classica ...
6.5
... if the opening has the same size of the de Bröglie wavelength of the electron, the electron will diffract like waves of wavelength λ diffract when passing an aperture of size similar to λ. ...
... if the opening has the same size of the de Bröglie wavelength of the electron, the electron will diffract like waves of wavelength λ diffract when passing an aperture of size similar to λ. ...
Lecture Q8
... having their electrons in different shells…instead of all down in the lowest energy state.) In the 1950’s with the development of Relativistic Quantum Mechanics came the theoretical proof for the Pauli Exclusion principle. ...
... having their electrons in different shells…instead of all down in the lowest energy state.) In the 1950’s with the development of Relativistic Quantum Mechanics came the theoretical proof for the Pauli Exclusion principle. ...
Chapter 2 - Las Positas College
... Solve: (a) Since Z = 4, the 9Be+ ion has 3 electrons, 4 protons, and 9 – 4 = 5 neutrons. (b) Since Z = 6, 12C has 6 electrons, 6 protons, and 12 – 6 = 6 neutrons. (c) Since Z = 7, the triply charged 15N+++ ion has 4 electrons, 7 protons, and 15 – 7 = 8 neutrons. ...
... Solve: (a) Since Z = 4, the 9Be+ ion has 3 electrons, 4 protons, and 9 – 4 = 5 neutrons. (b) Since Z = 6, 12C has 6 electrons, 6 protons, and 12 – 6 = 6 neutrons. (c) Since Z = 7, the triply charged 15N+++ ion has 4 electrons, 7 protons, and 15 – 7 = 8 neutrons. ...
The Quantum Mechanics of MRI
... • Pauli’s exclusion principle ensures that many shells are filled. • Nuclei with uneven (even) atomic number have half-integer (integer) spin • Nuclei with even atomic and mass numbers have zero spin. • Unpaired neutrons/protons provide the spin for MRI. ...
... • Pauli’s exclusion principle ensures that many shells are filled. • Nuclei with uneven (even) atomic number have half-integer (integer) spin • Nuclei with even atomic and mass numbers have zero spin. • Unpaired neutrons/protons provide the spin for MRI. ...
WORKSHEET 36: ATOMIC PROPERTIES
... 4. Which of the following elements (one from each pair) would you expect to have the highest first ionization energy? Explain your answers. (4) Ca and Be ...
... 4. Which of the following elements (one from each pair) would you expect to have the highest first ionization energy? Explain your answers. (4) Ca and Be ...
SEMESTER 1 EXAM Prblms/Short Ans
... Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbe ...
... Eq, S, U, SF – Equations; Show all equations used in all calculations. Steps; show each step leading to each answer. Units; show the appropriate units with each number used in all calculations. SF; Use the correct significant figures when expressing all answers. Use Scientific Notation for all numbe ...
The History of Quantum Mechanics
... or absorbed in discrete units, called quanta (quantized) • Gave the name “quantum”, which means “fixed amount,” to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted/absorbed as electromagnetic radiation • Awarded Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918 for this • *No major flaws or errors • This is regarde ...
... or absorbed in discrete units, called quanta (quantized) • Gave the name “quantum”, which means “fixed amount,” to the smallest quantity of energy that can be emitted/absorbed as electromagnetic radiation • Awarded Nobel Prize in Physics in 1918 for this • *No major flaws or errors • This is regarde ...
Problem set 5 - MIT OpenCourseWare
... In the uncoupled representation good quantum numbers correspond to the eigenvalues of the operators Ŝ12 , Ŝ22 , Ŝ1,z , Ŝ2,z . Since s1,2 = 12 while ms for each particle can take two values, we can list four possible states: |↑↑i, |↑↓i, |↓↑i, |↓↓i. c) Which quantum numbers would you use to label ...
... In the uncoupled representation good quantum numbers correspond to the eigenvalues of the operators Ŝ12 , Ŝ22 , Ŝ1,z , Ŝ2,z . Since s1,2 = 12 while ms for each particle can take two values, we can list four possible states: |↑↑i, |↑↓i, |↓↑i, |↓↓i. c) Which quantum numbers would you use to label ...
PHY801: Survey of Atomic and Condensed Matter Physics
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
... 4.1. Consider an atom with the 3 S1 ground state. What is the value of the Landé g-factor? Find the magnetization M as a function of magnetic field B (oriented along the z axis), the temperature T , and the concentration n = N/V . Show that in the limit of very high temperatures, where µB B << kB T ...
Figure 7.18 The 3d orbitals
... Figure 7.8 Three series of spectral lines of atomic hydrogen. Balmer is in the visible region and the other series, which have names also, are in uv or ir area of E-M radiation. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen atom 1. H atoms have only certain allowable energy levels called stationary states. 2. At ...
... Figure 7.8 Three series of spectral lines of atomic hydrogen. Balmer is in the visible region and the other series, which have names also, are in uv or ir area of E-M radiation. The Bohr Model of Hydrogen atom 1. H atoms have only certain allowable energy levels called stationary states. 2. At ...
Terms Used in Part 3
... the nucleus of the atom. The number of protons gives the atom its identity. Neutron: subatomic particle with no charge, the same mass as a proton, and located in the nucleus of the atom. Electron: subatomic particle with a negative charge and located outside the nucleus. Atomic number: the number of ...
... the nucleus of the atom. The number of protons gives the atom its identity. Neutron: subatomic particle with no charge, the same mass as a proton, and located in the nucleus of the atom. Electron: subatomic particle with a negative charge and located outside the nucleus. Atomic number: the number of ...
Chapter 4 Notes
... discrete amounts of energy • Electrons only lose energy when they move to a lower energy state ...
... discrete amounts of energy • Electrons only lose energy when they move to a lower energy state ...
General Chemistry - Valdosta State University
... Planck, Einstein, Energy and Photons Planck’s Equation - We can also say that light energy is quantized - This is used to explain the light given-off by hot objects. - Max Planck theorized that energy released or absorbed by an atom is in the form of “chunks” of light (quanta). E=hv h = planck’s co ...
... Planck, Einstein, Energy and Photons Planck’s Equation - We can also say that light energy is quantized - This is used to explain the light given-off by hot objects. - Max Planck theorized that energy released or absorbed by an atom is in the form of “chunks” of light (quanta). E=hv h = planck’s co ...
Hydrogen atom
A hydrogen atom is an atom of the chemical element hydrogen. The electrically neutral atom contains a single positively charged proton and a single negatively charged electron bound to the nucleus by the Coulomb force. Atomic hydrogen constitutes about 75% of the elemental (baryonic) mass of the universe.In everyday life on Earth, isolated hydrogen atoms (usually called ""atomic hydrogen"" or, more precisely, ""monatomic hydrogen"") are extremely rare. Instead, hydrogen tends to combine with other atoms in compounds, or with itself to form ordinary (diatomic) hydrogen gas, H2. ""Atomic hydrogen"" and ""hydrogen atom"" in ordinary English use have overlapping, yet distinct, meanings. For example, a water molecule contains two hydrogen atoms, but does not contain atomic hydrogen (which would refer to isolated hydrogen atoms).