SUMMARY OF FINAL QUESTIONS Assessment questions Jen T
... There were several horse ancestors discussed in class. Some features of the horse changed over time. What does this tell you about evolution? Several features were better adaptations to the environment; thus they were maintained in the gene pool. 3. Briefly describe how one of the main evolutionary ...
... There were several horse ancestors discussed in class. Some features of the horse changed over time. What does this tell you about evolution? Several features were better adaptations to the environment; thus they were maintained in the gene pool. 3. Briefly describe how one of the main evolutionary ...
Document
... The unequal survival and reproduction of organisms due to environmental forces, resulting in the preservation of favorable adaptations. ...
... The unequal survival and reproduction of organisms due to environmental forces, resulting in the preservation of favorable adaptations. ...
Chapter 13
... Evolution is a change in gene frequency in a population over time. 13.2 The Development of Evolutionary Thought 2. Why has Lamarck’s theory been rejected? Lamarck believed that acquired characteristics were passed to the next generation. Today we know that this is not true. 3. List five assumptions ...
... Evolution is a change in gene frequency in a population over time. 13.2 The Development of Evolutionary Thought 2. Why has Lamarck’s theory been rejected? Lamarck believed that acquired characteristics were passed to the next generation. Today we know that this is not true. 3. List five assumptions ...
Answers to Evolution Study Guide
... 33. Disruptive selection is a type of evolution that simultaneously favors individuals at both extremes of the distribution. When disruptive selection operates, individuals at the extremes contribute more offspring than those in the center, producing two peaks in the distribution of a particular tra ...
... 33. Disruptive selection is a type of evolution that simultaneously favors individuals at both extremes of the distribution. When disruptive selection operates, individuals at the extremes contribute more offspring than those in the center, producing two peaks in the distribution of a particular tra ...
Diversity of Life_4b
... • Evolution is descent with modification • Evolution occurs because individual organisms have genetic differences in their ability to find food, mates, avoid being eaten, in their metabolism and in countless other attributes • The best adapted individuals – those most successful at meeting the chall ...
... • Evolution is descent with modification • Evolution occurs because individual organisms have genetic differences in their ability to find food, mates, avoid being eaten, in their metabolism and in countless other attributes • The best adapted individuals – those most successful at meeting the chall ...
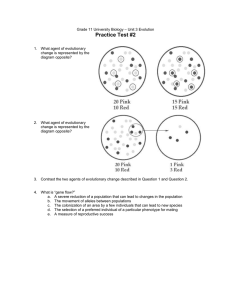
Grade 11 University Biology – Unit 3 Evolution
... 14. Which of the following statements best represents the power of Artificial Selection? a. Artificial selection reduces the number of harmful mutations that may occur b. Individuals that are very different from the original species can be produced in a controlled fashion c. Breeders typically breed ...
... 14. Which of the following statements best represents the power of Artificial Selection? a. Artificial selection reduces the number of harmful mutations that may occur b. Individuals that are very different from the original species can be produced in a controlled fashion c. Breeders typically breed ...
Evolution Reading questions from EOCT study Guide
... What did Lamarck believe caused changes in organisms over time? ...
... What did Lamarck believe caused changes in organisms over time? ...
Mechanisms of Evolution: Natural Selection
... leads to genetic material being shuffled. This shuffling, along with sexual reproduction, leads to variation within populations. This variation leads to selection, which ultimately leads to ...
... leads to genetic material being shuffled. This shuffling, along with sexual reproduction, leads to variation within populations. This variation leads to selection, which ultimately leads to ...
Ch16.3 Process of Speciation
... Princeton University decided to test Darwin’s hypothesis. They figured it relied on two testable assumptions. 1. Sufficient Variation among species 2. Natural Selection due to “fitness” of the variation ...
... Princeton University decided to test Darwin’s hypothesis. They figured it relied on two testable assumptions. 1. Sufficient Variation among species 2. Natural Selection due to “fitness” of the variation ...
Theory of Evolution notes to fill in
... will grow faster than the space and food to sustain it 1809 – Jean-Baptiste ________________ publishes his hypotheses about the inheritance of ______________ traits. His ideas were flawed, but his is the first to propose a mechanisms for evolution 1831 – _______________ sets sail on the Beagle, a vo ...
... will grow faster than the space and food to sustain it 1809 – Jean-Baptiste ________________ publishes his hypotheses about the inheritance of ______________ traits. His ideas were flawed, but his is the first to propose a mechanisms for evolution 1831 – _______________ sets sail on the Beagle, a vo ...
Four Historical Theories of Organic Change
... thought that species changed over time, and each developed a theory that explained how that change might occur. Why is Darwin’s mechanism, Natural Selection, still accepted (though modified) by today’s biologists, but Buffon’s and Lamarck’s theories are not? ...
... thought that species changed over time, and each developed a theory that explained how that change might occur. Why is Darwin’s mechanism, Natural Selection, still accepted (though modified) by today’s biologists, but Buffon’s and Lamarck’s theories are not? ...
Nothing in biology makes sense except in the light of evolution.
... among the individuals of a population, and that many of these traits are heritable. English economist Thomas Malthus’s essay pointed out the inevitable human suffering resulting from populations growing faster than supplies of resources. Darwin had personal knowledge of and interest in artificial ...
... among the individuals of a population, and that many of these traits are heritable. English economist Thomas Malthus’s essay pointed out the inevitable human suffering resulting from populations growing faster than supplies of resources. Darwin had personal knowledge of and interest in artificial ...
Evidence of Evolution
... reproduction. Individuals in populations vary. Some individuals are more suitable to a given environment and reproduce more easily and abundantly. The favored characteristics are passed to the next generation and the less-favored characteristics are not. ...
... reproduction. Individuals in populations vary. Some individuals are more suitable to a given environment and reproduce more easily and abundantly. The favored characteristics are passed to the next generation and the less-favored characteristics are not. ...
Who Wants To Live a Million Years Activity
... Part 3: Life in the wild is competitive, and organisms with the most beneficial traits will prosper. This is commonly known as “survival of the fittest”. Define the following term: Survival of the fittest - ...
... Part 3: Life in the wild is competitive, and organisms with the most beneficial traits will prosper. This is commonly known as “survival of the fittest”. Define the following term: Survival of the fittest - ...
1-31-13 Evolution PPT - Madison County Schools
... living species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from present day ones (the genetic changes in a population over generations) Scientific Theory – a well-supported explanation for some aspect of the natural world that includes many observations, inferences, and tested hypothese ...
... living species are descendants of ancestral species that were different from present day ones (the genetic changes in a population over generations) Scientific Theory – a well-supported explanation for some aspect of the natural world that includes many observations, inferences, and tested hypothese ...
Homework outline
... Darwin knew organisms in a population differed from each other, but he couldn’t explain how. Describe mutations and gene shuffling below and explain how they’re important for genetic variation. ...
... Darwin knew organisms in a population differed from each other, but he couldn’t explain how. Describe mutations and gene shuffling below and explain how they’re important for genetic variation. ...
Natural selection

Natural selection is the differential survival and reproduction of individuals due to differences in phenotype; it is a key mechanism of evolution. The term ""natural selection"" was popularised by Charles Darwin, who intended it to be compared with artificial selection, now more commonly referred to as selective breeding.Variation exists within all populations of organisms. This occurs partly because random mutations arise in the genome of an individual organism, and these mutations can be passed to offspring. Throughout the individuals’ lives, their genomes interact with their environments to cause variations in traits. (The environment of a genome includes the molecular biology in the cell, other cells, other individuals, populations, species, as well as the abiotic environment.) Individuals with certain variants of the trait may survive and reproduce more than individuals with other, less successful, variants. Therefore, the population evolves. Factors that affect reproductive success are also important, an issue that Darwin developed in his ideas on sexual selection, which was redefined as being included in natural selection in the 1930s when biologists considered it not to be very important, and fecundity selection, for example.Natural selection acts on the phenotype, or the observable characteristics of an organism, but the genetic (heritable) basis of any phenotype that gives a reproductive advantage may become more common in a population (see allele frequency). Over time, this process can result in populations that specialise for particular ecological niches (microevolution) and may eventually result in the emergence of new species (macroevolution). In other words, natural selection is an important process (though not the only process) by which evolution takes place within a population of organisms. Natural selection can be contrasted with artificial selection, in which humans intentionally choose specific traits (although they may not always get what they want). In natural selection there is no intentional choice. In other words, artificial selection is teleological and natural selection is not teleological.Natural selection is one of the cornerstones of modern biology. The concept was published by Darwin and Alfred Russel Wallace in a joint presentation of papers in 1858, and set out in Darwin's influential 1859 book On the Origin of Species, in which natural selection was described as analogous to artificial selection, a process by which animals and plants with traits considered desirable by human breeders are systematically favoured for reproduction. The concept of natural selection was originally developed in the absence of a valid theory of heredity; at the time of Darwin's writing, nothing was known of modern genetics. The union of traditional Darwinian evolution with subsequent discoveries in classical and molecular genetics is termed the modern evolutionary synthesis. Natural selection remains the primary explanation for adaptive evolution.