Organic Evolution
... On the archipelago of the Galapagos Islands, which most geologists believe to be of volcanic origin without ever having had any land connection with the west coast of South America, Darwin discovered a group of small finches. These birds have since been classified into more than a dozen species. The ...
... On the archipelago of the Galapagos Islands, which most geologists believe to be of volcanic origin without ever having had any land connection with the west coast of South America, Darwin discovered a group of small finches. These birds have since been classified into more than a dozen species. The ...
Evolution
... period of time. • Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. ...
... period of time. • Evolution is the process by which modern organisms have descended from ancient organisms. ...
Evolution Take
... Word Hints: adaptation, environment, mutation, natural selection 5. Our adult axolotl salamanders bred and produced around 500 eggs. Some of the eggs never hatched. Other offspring have died since hatching and now our population is down around 130 baby salamanders. In the natural world, even fewer w ...
... Word Hints: adaptation, environment, mutation, natural selection 5. Our adult axolotl salamanders bred and produced around 500 eggs. Some of the eggs never hatched. Other offspring have died since hatching and now our population is down around 130 baby salamanders. In the natural world, even fewer w ...
(D)evil Evolution Review Questions
... • Which scientist contributed to Darwin’s observation that too many organisms are produced in nature to be sustained? • Knowing and understanding scientific theories, would you say that natural selection can be quite different 100 years from now? Explain. • How did Darwin apply Lyell’s principles? ...
... • Which scientist contributed to Darwin’s observation that too many organisms are produced in nature to be sustained? • Knowing and understanding scientific theories, would you say that natural selection can be quite different 100 years from now? Explain. • How did Darwin apply Lyell’s principles? ...
Evolution_3
... Harvard University) admitted that if there were a population of 100 million individuals, and they produced a new generation every day, the likelihood of obtaining good evolutionary results from mutations could be expected once every 274 billion years! “Unless there is an unknown factor tremendously ...
... Harvard University) admitted that if there were a population of 100 million individuals, and they produced a new generation every day, the likelihood of obtaining good evolutionary results from mutations could be expected once every 274 billion years! “Unless there is an unknown factor tremendously ...
History of Life and Evolution ppt
... Darwin even found evidence that suggested species once present on earth had vanished. Researchers today speculate that 99.9% of all species that ever inhabited earth are now ...
... Darwin even found evidence that suggested species once present on earth had vanished. Researchers today speculate that 99.9% of all species that ever inhabited earth are now ...
Natural Selection
... Malay Archipelago. His journeys totaled more than 14,000 miles, and he collected over 125,000 ...
... Malay Archipelago. His journeys totaled more than 14,000 miles, and he collected over 125,000 ...
The Environment and Change Over Time
... Some finches flew back to the first island but could no longer interbreed with those finches (division) This process may have occurred over and over again as the finches flew to the other islands ...
... Some finches flew back to the first island but could no longer interbreed with those finches (division) This process may have occurred over and over again as the finches flew to the other islands ...
BLY 303 Lecture Notes, Guest Lecture 10/27/11 (O`Brien) Patterns in
... Where 2 branches diverge or split on “tree” indicates where an ancestral group split into 2 (sometimes more) descendent groups B. The only figure in Darwin’s Origin of Species was a hypothetical tree of life showing how lineages diverge from common ancestors ...
... Where 2 branches diverge or split on “tree” indicates where an ancestral group split into 2 (sometimes more) descendent groups B. The only figure in Darwin’s Origin of Species was a hypothetical tree of life showing how lineages diverge from common ancestors ...
EVOLUTION and NATURAL SELECTION
... • Developed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace • Is the cornerstone of modern evolutionary theory because it explains how biological change & adaptation occurs ...
... • Developed by Charles Darwin and Alfred Russell Wallace • Is the cornerstone of modern evolutionary theory because it explains how biological change & adaptation occurs ...
EVOLUTION- change in species over time
... -Using fossil evidence, he said that similar species come from a common ancestor -His hypothesis: Theory of Acquired Traits (“use it or lose it”) o States that traits are NOT determined by genes (DNA) Example: Ducks have webbed feet because they repeatedly stretch their toes, which caused webbed to ...
... -Using fossil evidence, he said that similar species come from a common ancestor -His hypothesis: Theory of Acquired Traits (“use it or lose it”) o States that traits are NOT determined by genes (DNA) Example: Ducks have webbed feet because they repeatedly stretch their toes, which caused webbed to ...
Process of Evolution
... In 1918-1919 there was an unusually high death rate associated with the influenza pandemic This flu virus had an interesting evolutionary nature as soldiers contracted a virus that was especially intense to the human immune system. Viruses are continually changing and therefore humans need to build ...
... In 1918-1919 there was an unusually high death rate associated with the influenza pandemic This flu virus had an interesting evolutionary nature as soldiers contracted a virus that was especially intense to the human immune system. Viruses are continually changing and therefore humans need to build ...
SBI3UI Name: Evolution Review Questions Answer the following
... Answer the following questions in full sentences in your notes to help you prepare for your Evolution Unit Test on Wed. Mar. 4. 1. Explain how the fossil record is evidence that not all life forms came into existence at the same time. 2. How did Lyell’s observations about changes in Earth’s geologic ...
... Answer the following questions in full sentences in your notes to help you prepare for your Evolution Unit Test on Wed. Mar. 4. 1. Explain how the fossil record is evidence that not all life forms came into existence at the same time. 2. How did Lyell’s observations about changes in Earth’s geologic ...
Only(features(that(result(from(common(ancestry(reflect( evolutionary
... and(other(regions(of(genomes(appear(to(evolve(at(constant( rates( • Average(rate(of(evolution:(number(of(genetic(differences( against(the(dates(of(evolutionary(branch(points(that(are(known( from(the(fossil(record( • Possibility(that(some(mutations(have(become(fixed(by(genetic( drift((neither(benefic ...
... and(other(regions(of(genomes(appear(to(evolve(at(constant( rates( • Average(rate(of(evolution:(number(of(genetic(differences( against(the(dates(of(evolutionary(branch(points(that(are(known( from(the(fossil(record( • Possibility(that(some(mutations(have(become(fixed(by(genetic( drift((neither(benefic ...
Evolution
... all types of organisms. Variation is present in species in nature • Artificial selection, nature provided the variation among different organisms, and humans selected those variations that they ...
... all types of organisms. Variation is present in species in nature • Artificial selection, nature provided the variation among different organisms, and humans selected those variations that they ...
Evolution Charles Darwin
... 1. According to Darwin, how do new species evolve? 2. Which individuals are most likely to survive to reproduce? 3. What is likely to happen to an individual that is poorly suited to its environment? 4. What sort of variation is inherited? Environmental? Genetic? Both? None? 5. Why do we have a good ...
... 1. According to Darwin, how do new species evolve? 2. Which individuals are most likely to survive to reproduce? 3. What is likely to happen to an individual that is poorly suited to its environment? 4. What sort of variation is inherited? Environmental? Genetic? Both? None? 5. Why do we have a good ...
Origin of Life
... Find where Lamarck is using his two laws to falsely explain evolution in this case. ...
... Find where Lamarck is using his two laws to falsely explain evolution in this case. ...
CHAPTER 23 LECTURE SLIDES Prepared by Brenda Leady
... scientists suggest life forms are not fixed George Buffon says life forms change over time Jean-Baptiste Lamarck realized that some animals remain the same while others change ...
... scientists suggest life forms are not fixed George Buffon says life forms change over time Jean-Baptiste Lamarck realized that some animals remain the same while others change ...
Evolution - Chapman @ Norquay School
... organisms were fixed and did not change. At this time there were a few scientists who were making major contributions to the study of biology. ...
... organisms were fixed and did not change. At this time there were a few scientists who were making major contributions to the study of biology. ...
WHAT DOES “EVOLUTION” MEAN?
... 1. All members of a species are NOT alike as Lamarck said. Great variation normally and naturally exists within a species. 2. Organisms cannot change most of their basic physical traits at will, even if survival depends on It. They cannot “adapt” because they need to. For example giraffes cannot mak ...
... 1. All members of a species are NOT alike as Lamarck said. Great variation normally and naturally exists within a species. 2. Organisms cannot change most of their basic physical traits at will, even if survival depends on It. They cannot “adapt” because they need to. For example giraffes cannot mak ...
Evolution=change
... increasing diversity and complexity of species • Taxonomy: classification of species • Common genes and proteins in all organisms--”the unity of life” • Adaptation of critters to environment--”the diversity of ...
... increasing diversity and complexity of species • Taxonomy: classification of species • Common genes and proteins in all organisms--”the unity of life” • Adaptation of critters to environment--”the diversity of ...
Biology Pre-Learning Check
... advantage or disadvantage compared to others in surviving and reproducing. The advantaged offspring are more likely to survive and reproduce. Therefore, the proportion of individuals that have advantageous characteristics will increase. When an environment changes, the survival value of some inherit ...
... advantage or disadvantage compared to others in surviving and reproducing. The advantaged offspring are more likely to survive and reproduce. Therefore, the proportion of individuals that have advantageous characteristics will increase. When an environment changes, the survival value of some inherit ...
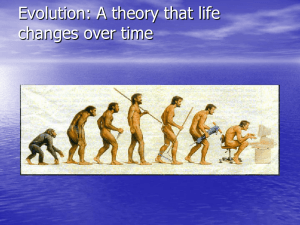
Evolution

Evolution is change in the heritable traits of biological populations over successive generations. Evolutionary processes give rise to diversity at every level of biological organisation, including the levels of species, individual organisms, and molecules.All of life on earth shares a common ancestor known as the last universal ancestor, which lived approximately 3.5–3.8 billion years ago. Repeated formation of new species (speciation), change within species (anagenesis), and loss of species (extinction) throughout the evolutionary history of life on Earth are demonstrated by shared sets of morphological and biochemical traits, including shared DNA sequences. These shared traits are more similar among species that share a more recent common ancestor, and can be used to reconstruct a biological ""tree of life"" based on evolutionary relationships (phylogenetics), using both existing species and fossils. The fossil record includes a progression from early biogenic graphite, to microbial mat fossils, to fossilized multicellular organisms. Existing patterns of biodiversity have been shaped both by speciation and by extinction. More than 99 percent of all species that ever lived on Earth are estimated to be extinct. Estimates of Earth's current species range from 10 to 14 million, of which about 1.2 million have been documented.In the mid-19th century, Charles Darwin formulated the scientific theory of evolution by natural selection, published in his book On the Origin of Species (1859). Evolution by natural selection is a process demonstrated by the observation that more offspring are produced than can possibly survive, along with three facts about populations: 1) traits vary among individuals with respect to morphology, physiology, and behaviour (phenotypic variation), 2) different traits confer different rates of survival and reproduction (differential fitness), and 3) traits can be passed from generation to generation (heritability of fitness). Thus, in successive generations members of a population are replaced by progeny of parents better adapted to survive and reproduce in the biophysical environment in which natural selection takes place. This teleonomy is the quality whereby the process of natural selection creates and preserves traits that are seemingly fitted for the functional roles they perform. Natural selection is the only known cause of adaptation but not the only known cause of evolution. Other, nonadaptive causes of microevolution include mutation and genetic drift.In the early 20th century the modern evolutionary synthesis integrated classical genetics with Darwin's theory of evolution by natural selection through the discipline of population genetics. The importance of natural selection as a cause of evolution was accepted into other branches of biology. Moreover, previously held notions about evolution, such as orthogenesis, evolutionism, and other beliefs about innate ""progress"" within the largest-scale trends in evolution, became obsolete scientific theories. Scientists continue to study various aspects of evolutionary biology by forming and testing hypotheses, constructing mathematical models of theoretical biology and biological theories, using observational data, and performing experiments in both the field and the laboratory. Evolution is a cornerstone of modern science, accepted as one of the most reliably established of all facts and theories of science, based on evidence not just from the biological sciences but also from anthropology, psychology, astrophysics, chemistry, geology, physics, mathematics, and other scientific disciplines, as well as behavioral and social sciences. Understanding of evolution has made significant contributions to humanity, including the prevention and treatment of human disease, new agricultural products, industrial innovations, a subfield of computer science, and rapid advances in life sciences. Discoveries in evolutionary biology have made a significant impact not just in the traditional branches of biology but also in other academic disciplines (e.g., biological anthropology and evolutionary psychology) and in society at large.