Lecture outline
... engines were thought of as unreliable (they were always blowing up), and costly to repair – not worth the risk. Instead, the growing manufacturing economy developed innovative machines which were small, portable, flexible and, most important, could be operated by hand, as the examples of the spinni ...
... engines were thought of as unreliable (they were always blowing up), and costly to repair – not worth the risk. Instead, the growing manufacturing economy developed innovative machines which were small, portable, flexible and, most important, could be operated by hand, as the examples of the spinni ...
World History (also in Honors)
... non-western worlds. Topics include: the rise of civilization; political, social and economic developments of the Middle Ages; the Renaissance and era of discovery; the growth of democracy and nationalism; the industrial revolution; and the two world wars. Postwar problems and recent developments are ...
... non-western worlds. Topics include: the rise of civilization; political, social and economic developments of the Middle Ages; the Renaissance and era of discovery; the growth of democracy and nationalism; the industrial revolution; and the two world wars. Postwar problems and recent developments are ...
Modern World History - DO YOU KNOW HISTORY?
... Course Description: This course will focus on how the world developed between Renaissance civilizations to the modern era. Also, emphasis will be placed on the personalities, events, and ideas that help influence our everyday lives. Course Objectives: This course will cover history and geography fro ...
... Course Description: This course will focus on how the world developed between Renaissance civilizations to the modern era. Also, emphasis will be placed on the personalities, events, and ideas that help influence our everyday lives. Course Objectives: This course will cover history and geography fro ...
World History Q2 Review
... 32. How did Camillo Cavour contribute to the Unification of Italy? 33. During the 18th and 19th centuries, increased contact between European and the continents of Africa, Asia, and South America resulted in? ...
... 32. How did Camillo Cavour contribute to the Unification of Italy? 33. During the 18th and 19th centuries, increased contact between European and the continents of Africa, Asia, and South America resulted in? ...
Ch25SAWTACCGS2015 - Marblehead High School
... -Why did cotton production in the American South skyrocket from 1790 to 1810? ...
... -Why did cotton production in the American South skyrocket from 1790 to 1810? ...
Syllabus for Mr. Klotzkin`s World History Class World History 5
... connections between World History and other content areas. Topics covered in this course include Exploration, the Age of Absolutism, the Enlightenment, the American Revolution, the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, Revolutions in Europe and Latin America, Life in the Industrial Age, Nati ...
... connections between World History and other content areas. Topics covered in this course include Exploration, the Age of Absolutism, the Enlightenment, the American Revolution, the French Revolution, the Industrial Revolution, Revolutions in Europe and Latin America, Life in the Industrial Age, Nati ...
Neolithic (Agricultural) Revolution: AP Analytical DBQ Rough Draft
... Although humans were hunter and gatherers during the Paleolithic Age, the development of agriculture and the creation of civilization were positive social, environmental and economic changes during the Neolithic Revolution. The historical evidence would indicate that the Neolithic Revolution and the ...
... Although humans were hunter and gatherers during the Paleolithic Age, the development of agriculture and the creation of civilization were positive social, environmental and economic changes during the Neolithic Revolution. The historical evidence would indicate that the Neolithic Revolution and the ...
MIDYEAR REVIEW TERMS, THEMES AND
... 1. Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in England, and why did it spread in the 1800s? 2. Describe three ways that city life changed in the later Industrial Revolution 3. What laws helped workers in ...
... 1. Why did the Industrial Revolution begin in England, and why did it spread in the 1800s? 2. Describe three ways that city life changed in the later Industrial Revolution 3. What laws helped workers in ...
The Industrial Revolution to the Contemporary World
... contrast the differences between revolutions in European countries such as France, Spain, and Great Britain to the American revolution. Then, they will tackle the Industrial Revolution and explore its origin and impact. The Industrial Revolution will lead into the age of imperialism as western natio ...
... contrast the differences between revolutions in European countries such as France, Spain, and Great Britain to the American revolution. Then, they will tackle the Industrial Revolution and explore its origin and impact. The Industrial Revolution will lead into the age of imperialism as western natio ...
File - Mr. Wathen Online Portal
... Changes in the Textile Industry As the demand for cloth grew, inventors came up with a series of remarkable inventions that revolutionized the British textile industry. The flying shuttle allowed weaves to work much faster. ...
... Changes in the Textile Industry As the demand for cloth grew, inventors came up with a series of remarkable inventions that revolutionized the British textile industry. The flying shuttle allowed weaves to work much faster. ...
Unit 3: Revolutionary Progress
... Format: - Chart of Enlightenment Thinkers & Ideas - Video: Biography of the Millennium, Enlightenment Thinkers - Primary Source Readings: Locke’s Second Treatise of Government; Frederick’s Essay on Government Day 5 – Quiz ...
... Format: - Chart of Enlightenment Thinkers & Ideas - Video: Biography of the Millennium, Enlightenment Thinkers - Primary Source Readings: Locke’s Second Treatise of Government; Frederick’s Essay on Government Day 5 – Quiz ...
World History Mini Research Paper
... 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, France, Germany, Japan, and the United States. Source: Green, Hank. “Coal, Steam, and the Industrial Revolution: Crash Course in History #32.” YouTube. 30 Aug. 2012. Web. 12 Oct. 2013. Annotation: Hank Green narrates an eleve ...
... 10.3 Students analyze the effects of the Industrial Revolution in England, France, Germany, Japan, and the United States. Source: Green, Hank. “Coal, Steam, and the Industrial Revolution: Crash Course in History #32.” YouTube. 30 Aug. 2012. Web. 12 Oct. 2013. Annotation: Hank Green narrates an eleve ...
Freshman World History World History, the requi
... World History, the required course for all freshmen, explores the economic and political roots of the modern world, the causes and consequences of the great military and economic events, and the rise of nationalism and the continuing persistence of political, ethnic, and religious conflicts around t ...
... World History, the required course for all freshmen, explores the economic and political roots of the modern world, the causes and consequences of the great military and economic events, and the rise of nationalism and the continuing persistence of political, ethnic, and religious conflicts around t ...
Industrial Revolution
... Movement – Rich landowners buy out poorer farmers and enclose/fence/hedge their property – Leaves many without jobs and food • Still need goods and now have a labor force ...
... Movement – Rich landowners buy out poorer farmers and enclose/fence/hedge their property – Leaves many without jobs and food • Still need goods and now have a labor force ...
By the late 1800s, Germany began to challenge Great Britain for
... How did Great Britain try to maintain its industrial superiority ? How and where did the United States begin to industrialize? What factors allowed other countries on the European continent to industrialize? What factors prevented some countries on the European continent from industrializing? How di ...
... How did Great Britain try to maintain its industrial superiority ? How and where did the United States begin to industrialize? What factors allowed other countries on the European continent to industrialize? What factors prevented some countries on the European continent from industrializing? How di ...
Example 1.
... income, such as the Cotton Gin, and as a result brought more people to different areas of the world causing social and political change that eventually revolutionized the whole world ending with products such as Imperialism, Nationalism and eventually leading to World War I. The Industrial Revolutio ...
... income, such as the Cotton Gin, and as a result brought more people to different areas of the world causing social and political change that eventually revolutionized the whole world ending with products such as Imperialism, Nationalism and eventually leading to World War I. The Industrial Revolutio ...
AP World History Study Guide Unit 5, Age of Revolution Name Part 2
... AP World History Study Guide Unit 5, Age of Revolution ...
... AP World History Study Guide Unit 5, Age of Revolution ...
Period 5 1750-1900 Industrial Revolution Greatest change in world
... Greatest change in world history since the Neolithic Revolution Effects felt in the following areas: Family life, communication, transportation, technology, environment, growth of cities, populations, social classes, science, art. Leads to: Imperialism, war, migration, political philosophies Industr ...
... Greatest change in world history since the Neolithic Revolution Effects felt in the following areas: Family life, communication, transportation, technology, environment, growth of cities, populations, social classes, science, art. Leads to: Imperialism, war, migration, political philosophies Industr ...
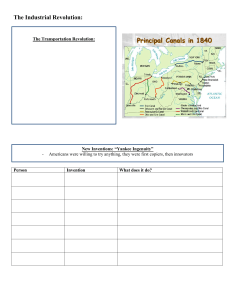
The Industrial Revolution:
... The transportation revolution o Turnpike o National road o Erie Canal System (map of principal canals of the 1840s) o Steamboat – robert fulton o Clipper ships o Railroads – immigrant labor (irish in the north east) New Inventions: “Yankee Ingenuity” o Ameircans were willing to try anything o They w ...
... The transportation revolution o Turnpike o National road o Erie Canal System (map of principal canals of the 1840s) o Steamboat – robert fulton o Clipper ships o Railroads – immigrant labor (irish in the north east) New Inventions: “Yankee Ingenuity” o Ameircans were willing to try anything o They w ...
Industrial Revolution - Discovery Education Store
... 2. Describe some of the earlier simple machines used in the manufacture of textiles in the cottage industry. How did they compare with the Flying Shuttle and the Spinning Jenny? 3. Outline the role of cloth merchants in the eighteenth century. 4. Why was there such a demand for textiles in Britain a ...
... 2. Describe some of the earlier simple machines used in the manufacture of textiles in the cottage industry. How did they compare with the Flying Shuttle and the Spinning Jenny? 3. Outline the role of cloth merchants in the eighteenth century. 4. Why was there such a demand for textiles in Britain a ...
The Industrial revolution promoted the world`s first industrial and
... For a few decades in the 19th century British manufactured goods dominated world trade. Most mass manufactured items were produced more efficiently and competitively in Britain than elsewhere. She also had the commercial, financial and political power to edge out rivals at home and abroad. In some i ...
... For a few decades in the 19th century British manufactured goods dominated world trade. Most mass manufactured items were produced more efficiently and competitively in Britain than elsewhere. She also had the commercial, financial and political power to edge out rivals at home and abroad. In some i ...
APWorldHistoryUnit11Vocabulary
... civilization’s focus in the 19th century shifted from the Enlightenment and Revolution to an emphasis on Nationalism and Industrial Productivity. AP World History Unit #11 - Nationalist Revolutions Sweep the West and The Industrial Revolution (Chapters 24-25) Instructions: This list is provided as a ...
... civilization’s focus in the 19th century shifted from the Enlightenment and Revolution to an emphasis on Nationalism and Industrial Productivity. AP World History Unit #11 - Nationalist Revolutions Sweep the West and The Industrial Revolution (Chapters 24-25) Instructions: This list is provided as a ...
Industrialization_Images_April_2016
... Late-1700s to mid-1800s What is it like to live in a society with rapidly changing technology? ...
... Late-1700s to mid-1800s What is it like to live in a society with rapidly changing technology? ...
B Day - Liberty Union High School District
... 1) How do you think merchants viewed their workers? 2) Why might the way merchants make money make landowners look down upon them? 3) Was destroying machines a good solution to the problem? 4) How would joining together in groups help workers win better conditions and higher pay? 5) Why do you think ...
... 1) How do you think merchants viewed their workers? 2) Why might the way merchants make money make landowners look down upon them? 3) Was destroying machines a good solution to the problem? 4) How would joining together in groups help workers win better conditions and higher pay? 5) Why do you think ...
A Day - Liberty Union High School District
... 1) How do you think merchants viewed their workers? 2) Why might the way merchants make money make landowners look down upon them? 3) Was destroying machines a good solution to the problem? 4) How would joining together in groups help workers win better conditions and higher pay? 5) Why do you think ...
... 1) How do you think merchants viewed their workers? 2) Why might the way merchants make money make landowners look down upon them? 3) Was destroying machines a good solution to the problem? 4) How would joining together in groups help workers win better conditions and higher pay? 5) Why do you think ...
Industrial Revolution

The Industrial Revolution was the transition to new manufacturing processes in the period from about 1760 to sometime between 1820 and 1840. This transition included going from hand production methods to machines, new chemical manufacturing and iron production processes, improved efficiency of water power, the increasing use of steam power, the development of machine tools and the rise of the factory system. It also included the change from wood and other bio-fuels to coal. Textiles were the dominant industry of the Industrial Revolution in terms of employment, value of output and capital invested; the textile industry was also the first to use modern production methods.The Industrial Revolution marks a major turning point in history; almost every aspect of daily life was influenced in some way. In particular, average income and population began to exhibit unprecedented sustained growth. Some economists say that the major impact of the Industrial Revolution was that the standard of living for the general population began to increase consistently for the first time in history, although others have said that it did not begin to meaningfully improve until the late 19th and 20th centuries.The Industrial Revolution began in Great Britain, and spread to Western Europe and North America within a few decades. Since then industrialisation has spread throughout the world. The precise start and end of the Industrial Revolution is still debated among historians, as is the pace of economic and social changes. GDP per capita was broadly stable before the Industrial Revolution and the emergence of the modern capitalist economy, while the Industrial Revolution began an era of per-capita economic growth in capitalist economies. Economic historians are in agreement that the onset of the Industrial Revolution is the most important event in the history of humanity since the domestication of animals, plants and fire.The First Industrial Revolution evolved into the Second Industrial Revolution in the transition years between 1840 and 1870, when technological and economic progress continued with the increasing adoption of steam transport (steam-powered railways, boats and ships), the large-scale manufacture of machine tools and the increasing use of machinery in steam-powered factories.