* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download ADAPTATIONS
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Inclusive fitness wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
The Descent of Man, and Selection in Relation to Sex wikipedia , lookup
Organisms at high altitude wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education in the United States wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of life wikipedia , lookup
Paleontology wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Vestigiality wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
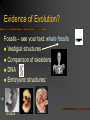
Evolution of Living Things Chapter 7 The teaching Evolution has been controversial… Evolution is also one of the most misunderstood and controversial concepts in the eyes of the general public. This situation is unfortunate, because the controversy surrounding evolution is unnecessary. Resistance to evolution stems in part from misunderstanding science and how it is distinct from religion. Science and religion provide different ways of knowing the Earth and universe. Science proceeds by testing hypotheses and thus is restricted to natural, testable explanations. By definition, science is unable to confirm or deny the existence or work of a Creator; such questions are beyond the realm of science. As a scientific concept, evolution therefore can make no reference to a Creator. Many people of faith, including scientists, find no conflict between evolution and their religion; in fact, many religious denominations have issued statements supporting evolution. Science and religion need not conflict. On a resume: “I studied a long time to become a Doctor, but I didn’t have any patience.” adaptation species evolution fossil fossil record vestigial structure trait selective breeding natural selection mutation generation time speciation adaptation vestigial structure adaptation adaptation vestigial structure natural selection fossil record endemic species Charles Darwin 1809-1882 British naturalist Gathered evidence for the theory of evolution during a 5 year “Voyage of the Beagle” around the world trip These islands sparked Darwin’s thoughts that led to his theory of: What’s so great about the Galapagos? 15+ separate islands with different climates and geography Isolated from South America by hundreds of miles of ocean Climates are controlled by different ocean currents that bombard the islands Off coast of Ecuador on the Equator Evidence of Evolution? Fossils – see your text: whale fossils Vestigial structures Comparison of skeletons DNA Embryonic structures: chicken cat human Fossils: Fossil Record: EVOLUTION THE PROCESS BY WHICH POPULATIONS ACCUMULATE INHERITED CHANGES OVER TIME GIVE SOME EXAMPLES FROM THE GALAPAGOS VIDEO: 1. 2. 3. ADAPTATIONS SOMETHING THAT HELPS AN ORGANISM SURVIVE Examples : … Darwin’s Finches: Natural Selection The process by which organisms with favorable traits survive and reproduce at a higher rate than organisms without the favorable trait Four Parts to “Natural Selection” 1 Overproduction: Each species produces more than will survive to reproduce. 2 Inherited variation Individuals in a population have slightly different traits. 3 Struggle to survive: Competition for limited resources. The KEY to natural selection… 4 Successful reproduction: Individuals better equipped for the environment survive and reproduce. Natural Selection (4 steps) 1 Overproduction 2 Genetic Variation 3 Struggle to Survive 4 Successful Reproduction Natural Selection in Action: COCKROACHES! Females lay almost 80 eggs. Average colony 1000 roaches . Potential for ________offspring! Genetic variation means… _____% will be killed by insecticide. ______% will reproduce and produce offspring ____________to insecticide. eeeeew! Generation time: the length of time from the birth of one generation to the birth of the next MAMMALS: long generation time INSECTS: short generation time Maximum Recorded Life Spans Mayfly: 3 hours Pygmy goby: 8 weeks Housefly: 6 months House mouse: 5 years Domestic dog: 29 years Domestic cat: 34 years Orangutan: 59 years African elephant: 80 years Human: 122 years Galápagos tortoise: 188 years Quahog clam: 220 years Maximum Recorded Life Spans Mayfly: 3 hours Pygmy goby: 8 weeks Housefly: 6 months House mouse: 5 years Domestic dog: 29 years Domestic cat: 34 years Orangutan: 59 years African elephant: 80 years Human: 122 years Galápagos tortoise: 188 years Quahog clam: 220 years As a rough guide, the numbers of currently identified species can be broken down as follows : 287,655 plants; 10,000 lichens; 1,190,200 invertebrates (including 950,000 insects); and 57,739 vertebrates, including 28,500 fishes, 5,743 amphibians, 8,163 reptiles, 9,917 birds, and 5,416 mammals. Adaptation to Pollution: Peppered Moth : Lived in England in two colors…dark and light colored. Dark were very RARE. After 1850, industrial revolution brought air pollution. After a while dark colored moths were better adapted. Moth color changed over time. Conditions of tree bark before 1850: Conditions after 1850: A Species… A group of organisms that can mate with one another to produce fertile offspring How do you get a new species? Florida panther bobcat kitty cat Formation of a new Species: 1. Separation 2. Adaptation 3. Division This is called speciation Also, many plants, and some animals, form hybrids in nature. Hooded crows and carrion crows look different, and largely mate within their own groups—but in some areas, they hybridize. Should they be considered the same species or separate species? One more cartoon…. Natural Selection: