* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecule Summary Chart
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
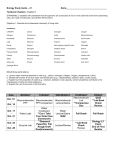
Macromolecule Summary Chart Macromolecule Carbohydrates Lipids Monomer(s) / Subunit(s) and Name of bond between adjacent monomers Types of this macromolecule and example(s) for each type Functions (Make sure they correspond to the type) Proteins Macromolecule Summary Chart Macromolecule Carbohydrates Monomer(s) / Subunit(s) and Name of bond between adjacent monomers Types of this macromolecule and example(s) for each type Monomer: Monosaccharides (Ex. glucose) 1. Monosaccharides (Ex. glucose, galactose, fructose) Energy storage 2. Disaccharides & Oligosaccharides (Ex. sucrose, lactose, maltose) Energy storage 3. Polysaccharides (Ex. starch, glycogen) Long term energy storage 4. Cellulose Cell structure: plant cell walls 5. Chitin Cell structure: cell walls in fungi & component of exoskeletons 1. Triglycerides (Fats) (Ex. vegetable oil, animal fat) Long-term energy storage, insulation, protection and cushioning of organs 2. Phospholipids (Ex. cell membrane) Amphophilic nature forms cell membrane (protects the cell and keeps its shape) 3. Steroids (Sterols) (Ex. cholesterol, estrogen, testosterone) Maintains fluidity of cell membrane, cell signaling, hormones 4. Waxes (Ex. cutin, beeswax) Water-proofing Type of bond: Glycosidic linkage Lipids Monomer: Glycerol and fatty acids Type of bond: Ester linkage Functions (Make sure they correspond to the type) Proteins Monomer: Amino acids Type of bond: Peptide bond ** Do not worry about the different types of proteins ** Some examples: Enzymes, silk, actin/myosin (muscle protein), keratin (hair/nail protein), hemoglobins, antibodies, etc. Enzymes: catalyze chemical reactions Keratin/Silk: structural support Actin/Myosin: movement of body (via muscles) Hemoglobin; transportation of oxygen in blood to target cells Antibodies: defend body from foreign invaders and fight off bacteria and viruses Some proteins are also involved in cell regulation and turning on/off genes.