* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mr - Hightower Trail
Survey
Document related concepts
Growing Up in the Universe wikipedia , lookup
Objections to evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sociocultural evolution wikipedia , lookup
Sexual selection wikipedia , lookup
Unilineal evolution wikipedia , lookup
Hologenome theory of evolution wikipedia , lookup
Evidence of common descent wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Natural selection wikipedia , lookup
Creation and evolution in public education wikipedia , lookup
Acceptance of evolution by religious groups wikipedia , lookup
Catholic Church and evolution wikipedia , lookup
Punctuated equilibrium wikipedia , lookup
Genetics and the Origin of Species wikipedia , lookup
Transitional fossil wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
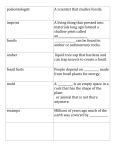
Mr. Blacher’s 7th Biology My Study Guide for: Evolution I. Vocabulary: 1.Species 2.Adaptations 3. Evolution 4. Natural Selection 5. Overproduction 6. Competition 7. Variation II. 8. Selection 9. Continental Drift 10. Theory 11. Law 12. Fossil (Absolute and Relative Dating) 13. Sedimentary 14. Homologous Structures Charles Darwin: Who was this guy and what did he observe in the Galapagos Islands? What did he learn from the finches of the Galapagos? How did he explain what he saw? III. Natural Selection What is it? What are the four factors that influence this process? How does it lead to evolution? What happened to the peppered moths during the Industrial Revolution? How does this illustrate natural selection? IV. Evolution What is the role of genetics in this process? How can new species arise (Geographic isolation, AKA-allopatric speciation)? What evidence is there for evolution (DNA, homologous structures, similarities in embryonic (pre-birth) development)? Branching tree diagrams…what do they show? V. Fossils and the Fossil Record What are petrified fossils, molds, casts, and preserved remains? How can we tell how old fossils are (relative and absolute dating methods)? What is half-life and how do we use it to date rocks and fossils? What is the key to effective selection of isotopes for radiometric dating? What is the geologic time scale and which period of time is the longest one within it? How old is the Earth? VI. How long does Evolution take? What is Gradualism? What is Punctuated Equilibrium? Practice Questions: 1. During the Great Migration in the Serengeti, many of the grazing herbivores don’t survive…many do. Use what you know about natural selection to explain what is taking place. Can you think of another situation in the natural world wherein this takes place? 2. How do genetics, natural selection, and evolution all interrelate? 3. There are 10 grams of carbon-14 in a rock at time=zero. How much time will have passed, and how much carbon-14 will remain in the rock after three half-lives? 4. You have found a fossil of a trilobite, which is an extinct arthropod that first appeared in the Cambrian period (this period ended about 488 mya). You may borrow the equipment to measure Carbon14/Nitrogen or the equipment to measure Uranium-235/Lead-207. Which equipment would you borrow to attempt to date this fossil and why?