* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Janeway's Immunology
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Plant disease resistance wikipedia , lookup
Adoptive cell transfer wikipedia , lookup
Common cold wikipedia , lookup
Complement system wikipedia , lookup
Sociality and disease transmission wikipedia , lookup
Cancer immunotherapy wikipedia , lookup
Autoimmunity wikipedia , lookup
Molecular mimicry wikipedia , lookup
Vaccination wikipedia , lookup
Gluten immunochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Hygiene hypothesis wikipedia , lookup
Immunocontraception wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Immune system wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive immune system wikipedia , lookup
Immunosuppressive drug wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Innate immune system wikipedia , lookup
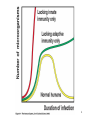
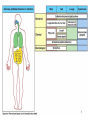
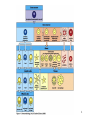
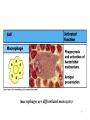
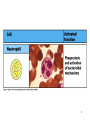
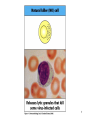
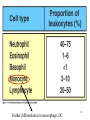
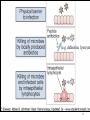
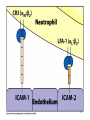
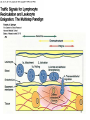
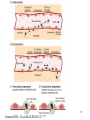
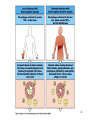
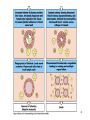
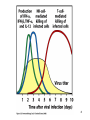
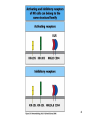
Biophysical Immunology Laboratory Thomas Vorup-Jensen Institute for Medical Microbiology and Immunology University of Aarhus Denmark [email protected] Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture I:(mainly) Cellular factors Important messanges: Important cell types supporting innate immunity effector functions Important molecular mechanisms in leukocyte functions Molecules of microbial origin triggering an innate immune response 2 Innate immunity: a role everywhere in the immune system Humoral Immune response Chap. 10 Cell mediated immunity Chap. 8&9 INNATE IMMUNITY Antigen capture Chap. 4-6 Immune pathogenesis (autoimmunity & cancer) Several chap. 3 Figure 8-1 4 Figure 8-6 5 6 (macrophages are diffrentiated monocytes) 7 8 9 Further differentiation to macrophage, DC 10 (e.g. defensins, lysozym 11 Time (adaptive immunity) 12 13 14 15 16 Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture I:(mainly) Cellular factors Important message !: Innate immunity protects the body against infection in the early phases of infection Damage to the host may occur as a consequence of innate immunity effector functions – inflammation may be excessive 17 How to trigger the complement system: Discrimination between self and non-self by pattern recogniti Janeway (1989) Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 54:1-13 18 19 20 Mogensen (2010) Clin. Rev. Microbiol. 22: 240-273 22 23 24 Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture I:(mainly) Cellular factors Important message !: Many molecules in innate immunity recognize ”patterns” on microbial surfaces. This recognition leads to triggering on the immune response. 25 26 27 28 29 Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture I:(mainly) Cellular factors Important message !: Innate immunity triggers the production bactericidal compounds and cytokines that control cell migration 30 31 32 33 34 35 37 38 Downloaded from: StudentConsult (on 29 October 2007 04:52 PM) © 2005 Elsevier 39 Carman (2009), J Leuk Biol 122:3025-35 40 41 Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture I:(mainly) Cellular factors Important message !: Adhesion molecules play an important role in supporting contact between leukocytes and inflammed tissue during migration and phagocytosis. 42 43 Viruses: typically a job for the aqcuired immune system 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 …to be continued Innate Immunity Janeway’s Immunobiology Chapter 2&3 Lecture II:(mainly) Soluble (humoral) factors Important messages: Important soluble molecules supporting innate immunity effector functions Connection between molecular structure and function in the immune system 52