* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Membrane
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
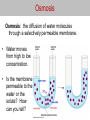
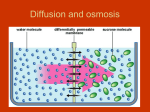
Osmosis Osmosis: the diffusion of water molecules through a selectively permeable membrane. • Water moves from high to low concentration. • Is the membrane permeable to the water or the solute? How can you tell? Osmosis Tonicity: Determines the direction of water movement due to osmosis. • Hypertonic: the solution with a greater concentration of the solute. – A cell would lose water and shrink if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Plasmolysis: when the cell membrane of a plant cell pulls away from the cell wall. – Causes the plant to wilt due to a lack of osmotic pressure. Osmosis Tonicity: Determines the direction of water movement due to osmosis. • Hypertonic: the solution with a greater concentration of the solute. – A cell would lose water and shrink if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Plasmolysis: when the cell membrane of a plant cell pulls away from the cell wall. – Causes the plant to wilt due to a lack of osmotic pressure. Osmosis • Hypotonic: the solution with the lesser concentration of the solute. – A cell would gain water and swell if it is placed in a hypertonic solution. – Cytolysis: when a cell bursts because of osmotic pressure. – Turgor Pressure: the pressure created when the cell membrane pushes against a cell wall. Osmosis • Isotonic: concentration of the solute is the same on both sides of the membrane (equilibrium). – Cells will stay the same size in a isotonic solution, there is no net movement of water molecules. http://www.glencoe.com/sites/common_ass ets/science/virtual_labs/LS03/LS03.html 10% NaCL 90% H2O CELL 20% NaCL 80% H2O What is the direction of water movement? Cell in Hypertonic Solution 15% NaCL 85% H2O ENVIRONMENT CELL 5% NaCL 95% H2O What is the direction of water movement?