* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Types of Solutions
Survey
Document related concepts
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
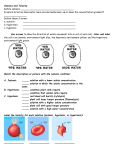
There are three types of solutions relating to the effects of osmosis on cells Everything is in relation to the cell Hypertonic Solution In a hypertonic solution, the solution has a higher solute concentration than that of the cell As a result the water will leave the cell When cells are in a hypertonic solution Animal cells will shrink Plant cells will have a collapsed vacuole Hypotonic Solution In a hypotonic solution, When cells are in a the solution has a lower solute concentration than the solute concentration inside the cells. The water as a result will enter the cell. hypotonic solution Animal cells would swell and can burst. The vacuoles of the plant cell will swell, and the contents of the cell will be pushed against the cell wall Isotonic Solution In an isotonic solution, the concentrations of solutes are the same inside the cell as it is outside the cell. The cell would not lose water, nor will it gain water. Diffusion vs. Osmosis Diffusion- is the net movement from regions of greater concentration to the regions of lesser concentration. Osmosis- is the diffusion of water. It depends on the number of solute particles present.