* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous Systems - manorlakesscience
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Neurogenomics wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Dual consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Lateralization of brain function wikipedia , lookup
Causes of transsexuality wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Neurotechnology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Sports-related traumatic brain injury wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Spinal cord wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
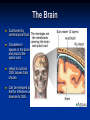
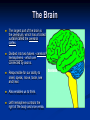
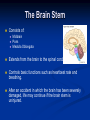
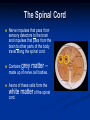
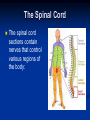
Nervous Systems Aims: Must be able to state the main components of the nervous system. Should be able to describe and explain the structure of the Brain. Could be able to describe and explain the structure of the Spinal Cord. Structure of Nervous System Central Nervous System – BRAIN SPINAL CORD Peripheral Nervous System – SENSORY (Afferent) – Information into CNS from external and internal environments. Motor (Efferent) – Information away from the CNS Subsections Sensory – Somatic – Information from external environments via sense organs, e.g. Eyes Visceral – Information from internal environments, e.g. Heart Motor – Autonomic (involuntary) – Signals that regulate internal environments – Parasympathetic and Sympathetic Somatic (voluntary) – Signals to Skeletal muscles The Brain Cushioned by cerebrospinal fluid. Circulates in spaces in the brain and around the spinal cord. Helps to cushion CNS tissues from shocks. Can be removed to test for infections or disease to CNS. The Brain The largest part of the brain is the cerebrum, which has a folded surface called the cerebral cortex. Divided into two halves - cerebral hemispheres - which are connected by axons. Responsible for our ability to smell, speak, move, taste, see and hear. Also enables us to think. Left hemisphere controls the right of the body and vice versa. Cerebrum The Hypothalamus The Thalamus Receives impulses from sensory neurons. Regulates the release of many hormones. Directs them to the various parts of the brain where they are interpreted. Controls many other aspects of homeostasis. Plays a role in temperature maintenance, water balance and blood pressure as well as sensations such as hunger and thirst. Plays a key role in memory, maintaining sensation, motor (movement) activities. The Brain Stem Consists of: Midbrain Pons Medulla Oblongata Extends from the brain to the spinal cord. Controls basic functions such as heartbeat rate and breathing. After an accident in which the brain has been severely damaged, life may continue if the brain stem is uninjured. The Spinal Cord Nerve impulses that pass from sensory detectors to the brain and impulses that pass from the brain to other parts of the body travel along the spinal cord. Contains grey matter – made up of nerve cell bodies. Axons of these cells form the white matter of the spinal cord. The Spinal Cord The spinal cord sections contain nerves that control various regions of the body: Activity Answer the questions from pages 93 and 94 in the Biozone book.