* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 2, section 2
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
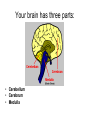
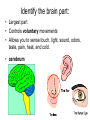
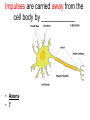
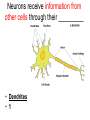
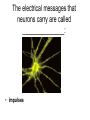
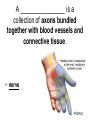
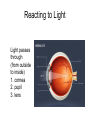
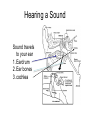
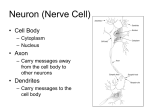
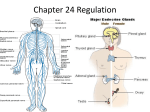
Chapter 25, section 1 The Nervous System Nervous System • Two functions 1. Gathers and interprets ______ • Information 2. __________ to information gathered • Responds The Nervous System has two parts. • • • • Central Nervous System (CNS) brain and spinal cord Peripheral System (PS) all of the parts of the nervous system except the ______ and _________ • Brain, Spinal cord • PS uses specialized structures called ______ • nerves Sensory Neurons • Gather information about what’s happening in and around your body • Use ________ • Receptors • ______ neurons send impulses from the brain and spinal cord to other systems • motor Motor Neurons • Send impulses from the ______ down the spinal cord to parts of the body • brain • Make the body do stuff (action!) Your brain has three parts: • Cerebellum • Cerebrum • Medulla Identify the brain part: • Connects to your spinal cord • Controls involuntary processes: body temperature, heart rate, blood pressure • medulla Identify the brain part: • Second-largest part • Helps you maintain your balance • cerebellum Identify the brain part: • Largest part • Controls voluntary movements • Allows you to sense touch, light, sound, odors, taste, pain, heat, and cold. • cerebrum A _____________ is a nerve cell that is able to transfer messages in the form of fast-moving electrical energy: • neuron Impulses are carried away from the cell body by ____________ • Axons • 7 Neurons receive information from other cells through their _________ • Dendrites • 1 The electrical messages that neurons carry are called _______________: • impulses A ________________ is a collection of axons bundled together with blood vessels and connective tissue. • nerve Spinal cord • Is protected by vertebrae Homeostasis • Keeping all body’s functions in balance • Sympathetic and parasympathetic systems working together to maintain homeostasis Papillae • Tiny bumps on your tongue • Contain taste buds Receptors • Skin has different kinds of receptors • There are receptors for pressure temperature pain vibration Feedback mechanism • Cycle of events in which information from one step controls or affects a previous step EX: Cooling process of your body Reacting to Light Light passes through (from outside to inside) 1. cornea 2. pupil 3. lens Hearing a Sound Sound travels to your ear 1. Eardrum 2. Ear bones 3. cochlea Olfactory Cells • Upper part of the nasal cavity • Sensory reactors for smell