* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nerve Impulses ppt
Neural modeling fields wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Patch clamp wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Action potential wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Resting potential wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
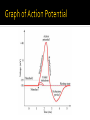
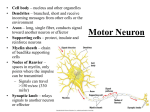
HOW MESSAGES ARE SENT A message travelling down a neuron It comes from: Another neuron A sensory receptor Also called an ACTION POTENTIAL Sodium (Na+) Potassium (K+) Since both are positive…. Its all relative Positive = more positive ions Negative = fewer positive ions Not sending an impulse Neuron impermeable to Na+ Na+ collects outside Potassium moves freely (permeable) Outside is positive All Na+ and some K+ Inside is negative Some K+ Polarized Na+ channels (gates) open Neurons now permeable to Na+ Na+ diffuse into cell Polarity reversed Inside positive Outside negative Depolarized K+ moving out of the cell (closes Na+ gates) Depolarization occurs in a small area Affects adjacent gates ▪ Creates “wave” of electricity ▪ Travels length of axon Na+ gates are only open for a fraction of a second Na+ gets trapped inside the cell Recovery period Few thousandths of a second Neuron cannot be stimulated again Neuron must ne returned to “resting potential” Sodium potassium pumps returns membrane to rest Na+ moves out K+ moves in Repolarized Outside now + Inside now - Myelinated neuron Faster transmission (100 m/s) 2m/s (unmyelinated) Jumps from one node of Ranvier to next Uses less energy Minimum strength stimulus required for action potential to occur Different for each neuron Impulses are all alike once threshold reached Strength only changes with number sent