* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download THE BRAIN - Dublin City Schools
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Blood–brain barrier wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Neuroinformatics wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
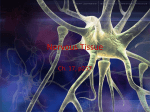
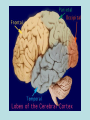
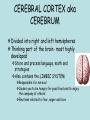
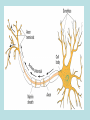
THE BRAIN AND THE EFFECTS OF ALCOHOL AND OTHER DRUGS THE BRAIN Command center of your body Weighs about 3 pounds Different centers which control different things Despite being 90-95 percent of its adult size by age six, the brain is still “under construction” until age 18. BRAIN STEM Vital life center Controls breathing, swallowing, heart beat, sleeping The things you never think about Gulping large amounts of alcohol in a short time can stop the breathing reflex and cause death CEREBELLUM Is responsible for things you learn once and never have to think about again: Walking, riding a bike, throwing a ball Higher thought processes like music and complex math problems Changes drastically during teen years, increasing its number of nerve cells and connections to the rest of the brain What Do They Do? • Frontal Lobe – Reasoning, planning, parts of speech, movement, emotions, and problem solving • Parietal Lobe – Movement, orientation, recognition, perception of stimuli • Occipital Lobe – Visual processing Temporal Lobe – Perception and recognition of auditory stimuli, memory, and speech CEREBRAL CORTEX aka CEREBRUM Divided into right and left hemispheres Thinking part of the brain- most highly developed Store and process language, math and strategies Also contains the LIMBIC SYSTEM Responsible for survival Causes you to be hungry for good food and to enjoy the company of others; Emotions related to fear, anger and love LIMBIC SYSTEM Hippocampus and Amygdala Memory • Drugs can have powerful control of the brain stem and limbic system. • These systems can override our cortex in controlling our behavior. So, we do things without thinking! Structure of a Neuron • 5 PARTS 1. Dendrites = receive messages, many fibers 2. Cell Body = directs all activities of the neuron 3. Axon = send messages, long single fiber 4. Myelin Sheath = insulation and speed of signal transfer 5. Axon Terminals = release neurotransmitter MYELIN A fatty substance that covers axons. The more myelin an axon has, the faster nerve impulses can travel. – After puberty, the amount of myelin in the brain increases dramatically, making the brain much more efficient. NEUROTRANSMISSION = • The transfer of a message (electrical impulse “aka” chemical release) from the axon of one nerve cell to the dendrites of another Neurotransmitters – Chemical messengers carrying information from one neuron to another • Types of Neurotransmitters = – Serotonin (associated with depression) – Dopamine (associated with depression) How Neurons Communicate • Axon terminals release neurotransmitter (chemical release) – Neurotransmitters going into the space between the axon and dendrites called the synapse. • Neurotransmitter enters synapse – Binds to receptors in the dendrites that fit “Lock & key”



















![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)