* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 8: Sensation and Perception
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
End-plate potential wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Donald O. Hebb wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neurotransmitter wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Nonsynaptic plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Chemical synapse wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
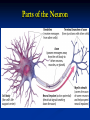
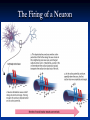
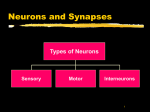
Unit 3: Biological Bases of Behavior Mr. McCormick A.P. Psychology Essential Question How are human thought and behavior affected by the following: • • • • The Nervous System The Endocrine System The Brain Genetics Unit 3-A (A): The Neuron Mr. McCormick A.P. Psychology Do-Now (Discussion) What is Biological Psychology? What parts of the body do Biological Psychologists primarily study? In understanding psychology, why do you think it is important to understand biological processes? Biological Psychology Biological Psychology: A branch of Psychology concerned with the links between biology and behavior Biological Psychologists: Behavioral Neuroscientists Neuropsychologists Behavior Geneticists Physiological Psychologists Biopsychologists Biological Psychology The Neuron Neuron: Nerve cell Basic building block of the nervous system The Neuron Types of Neurons: Sensory Neurons: Motor Neurons: Carry incoming information from sensory receptors to the brain/spinal cord E.g. Perceiving something as “hot” Carry outgoing information from the brain/spinal cord to the muscles/glands E.g. Clenching a fist Interneurons: Located within the brain/spinal cord Communicate internally between sensory inputs and motor outputs E.g. Reflexes The Neuron Provide an example of information that sensory neurons may transmit. Provide an example of information that motor neurons may transmit. Provide an example of information that interneurons may transmit. Parts of the Neuron The Firing of a Neuron Neurons transmit messages when stimulated by our senses, or triggered by chemicals of other neurons Resting Potential: Threshold: Fluid interior of axon: negatively charged ions Fluid exterior of axon membrane: positively charged ions Level of stimulation required to trigger a neural impulse (action potential) Excitatory signals (accelerator) minus inhibitory signals (brakes) must reach minimum intensity Action Potential: Neural impulse Depolarization occurs Brief electrical charge that travels down an axon “All-or-None” Response The Firing of a Neuron Review What is a neuron? Differentiate between the 3 types of neurons: Discuss the functions of the following parts of the neuron: Sensory Neurons Motor Neurons Interneurons Dendrites Axon Myelin Sheath Terminal Branches What causes neurons to fire? Homework Research Study # 2: “More Experience = Bigger Brain” (Pgs. 11-18) Unit 3-A FRQ: Unit 3-A Quiz: “The Neuron”