* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience and intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Functional magnetic resonance imaging wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Artificial general intelligence wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Pre-Bötzinger complex wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
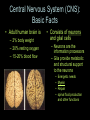
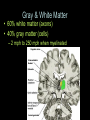
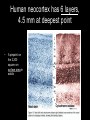
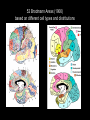
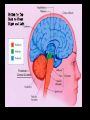
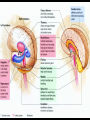
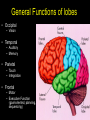
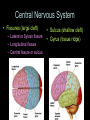
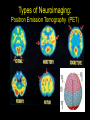
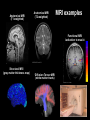
Central Nervous System (CNS): Basic Facts • Adult human brain is – 2% body weight – 20% resting oxygen – 15-20% blood flow • Consists of neurons and glial cells – Neurons are the information processors – Glia provide metabolic and structural support to the neurons • • • • Energetic needs Myelin Repair spinal fluid production and other functions Size of Adult Human Brain • Range: 1000 to 2000 grams • Average male = 1,350 g • Average female = 1,200 g • Anatole France = 1,000 g (20th century poet) • Albert Einstein = 1,230 g • Lord Byron = 2,380 g (Romance poet) Neurons • 200 cell types • 10 trillion cells in head • 25 billion pyramidal neurons, connects to 1000s of other neurons Gray & White Matter • 60% white matter (axons) • 40% gray matter (cells) – 2 mph to 250 mph when myelinated Neural Structure Human neocortex has 6 layers, 4.5 mm at deepest point • A pinpoint on the 2,200 square cm surface area in adults 52 Brodmann Areas (1906) based on different cell types and distributions Bottom to Top Back to Front Right and Left Forebrain = Cortex & Limbic General Functions of lobes • Occipital – Vision • Temporal – Auditory – Memory • Parietal – Touch – Integration • Frontal – Motor – Executive Function (goal-oriented, planning, sequencing) Central Nervous System • Fissures (large cleft) – Lateral or Sylvan fissure – Longitudinal fissure – Central fissure or sulcus • Sulcus (shallow cleft) • Gyrus (tissue ridge) Types of Neuroimaging: Positron Emission Tomography (PET) Anatomical MRI (T1-weighted) Anatomical MRI (T2-weighted) MRI examples Functional MRI (activation to music) Structural MRI (gray matter thickness map) Diffusion Tensor MRI (white matter tracts) Electroencephalography (EEG) – Brainwaves