* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Lesson 1.1
Survey
Document related concepts
Foundations of mathematics wikipedia , lookup
History of logarithms wikipedia , lookup
Numbers (TV series) wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Law of large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Collatz conjecture wikipedia , lookup
Proofs of Fermat's little theorem wikipedia , lookup
Surreal number wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
Numbers, Data, and
Problem Solving
Lesson 1.1
Sets of Numbers
Natural Numbers
The whole numbers
The counting numbers
{ 1, 2, 3, 4, … }
The counting numbers with zero included
{ 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, … }
The integers
The whole numbers and their additive opposites,
their negatives
{ . . . , -4, -3, -2, -1, 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, … }
Sets of Numbers
Rational numbers
Any number expressed as the quotient of two
integers – and the denominator is NOT zero
Note: these can be
written as terminating or
repeating decimals
p
q
where p and q Integers, and q 0
Irrational numbers
Numbers that cannot be represented by quotient of
two integers
2
e sin 37
Try it Out …
Classify the following numbers as
Natural numbers
Whole numbers
Rationals
Irrationals
17
3
17
5280
3.14
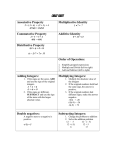
Order of Operations
1.
2.
3.
Work from innermost parentheses, out
Evaluate all exponents
Multiplications, divisions from left to right
Additions and subtractions from left to right
10 6
4 2(4 5) 2
53
13 9 16
57
3
Calculating Percent Change
If a quantity changes from c1 to c2 the percent of
change is given by:
c2 c1
100
c1
Gasoline changed from $1.19 to $1.43 in one
week's time … what was the percent of
increase?
Calculating Percent Change
What if you are told the percentage of increase
and the original value … now find the new
value!
c2 c1
100
c1
Enter the values you know
Solve for the value you don't know
What kinds of numbers
did we use in these
calculations?
What if gas was at $1.47 and went down by
12% a week later. What is the new price?
Problem Solving
Important strategies …
Draw a sketch
Write formulas involved
Determine values in the formulas that you know
Solve for the values you are searching for
The Milky Way has a diameter of 6 x 1017 miles.
If the speed of light is 186,000 miles/sec, how
many years does it take for light to travel across
the galaxy?
Assignment
Lesson 1.1
Page 10
Exercises
1 – 27 odd, 77 - 87odd