* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cognitive Information Processing
Stephen Grossberg wikipedia , lookup
Interference theory wikipedia , lookup
Procedural memory wikipedia , lookup
Bioecological model wikipedia , lookup
Exceptional memory wikipedia , lookup
Personal information management wikipedia , lookup
Sparse distributed memory wikipedia , lookup
Information wikipedia , lookup
Source amnesia wikipedia , lookup
Catastrophic interference wikipedia , lookup
Effects of alcohol on memory wikipedia , lookup
Social learning in animals wikipedia , lookup
Collective memory wikipedia , lookup
Adaptive memory wikipedia , lookup
Information audit wikipedia , lookup
Socioeconomic status and memory wikipedia , lookup
Childhood memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive model wikipedia , lookup
Misattribution of memory wikipedia , lookup
Background music wikipedia , lookup
Visual selective attention in dementia wikipedia , lookup
Mind-wandering wikipedia , lookup
Prenatal memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
Memory and aging wikipedia , lookup
Music-related memory wikipedia , lookup
Eyewitness memory (child testimony) wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive interview wikipedia , lookup
Atkinson–Shiffrin memory model wikipedia , lookup
Dual process theory wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Subvocalization wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy of memory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive psychology wikipedia , lookup
Neo-Piagetian theories of cognitive development wikipedia , lookup
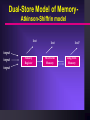
Instructional Technology 6260 Cognitive Information Processing Theory Cognitive Information Processing Without looking at one, draw a picture of a penny Without looking at it, try to describe your watch: what color is the face what marks the hours what color are the hands is there a second hand does it say anything on the face Assumptions of Human Information Processing Some learning processes are unique to humans Mental events are the focus of study The study of human learning must be objective and scientific Individuals are actively involved in the learning process Learning involves the formation of mental associations that are not necessarily reflected in overt behavior changes Knowledge is organized Learning is a process of relating new information to previously learned information Terminology Cognitive Process- any internal mental event and includes such phenomena as perceiving, attention, interpretation, understanding and remembering Learning vs. Memory - learning is viewed as the acquisition of new information. Memory is related to the ability to recall information that has been previously learned Storage - the process by which new information is placed in memory Retrieval - the process by which people “find’ the information they have previously stored so they can use it again Encoding - the process by which information is modified before it is stored - often helps storage Dual-Store Model of MemoryAtkinson-Shiffrin model lost input input input Sensory Register lost Short-term Memory lost? Long-term Memory Sensory Register capacity form of storage duration The Role of Attention the process by which people select some of the environmental input they receive for further cognitive processing What do you see????? Factors Influencing Attention Size Intensity Novelty Incongruity Emotion Personal Significance Competition between similar tasks Which letters first draw your attention? aB cD Read the Italics Print... Somewhere Among hidden the in most the spectacular Rocky Mountains cognitive near abilities Central City is Colorado the an ability old to miner select hid one a message box from of another gold. We Although do several this hundred by people focusing have our looked attention for on it, certain they cues have such not as found type it style. Incongruity I took a walk to the rabbit this morning. Processes Underlying Attention selective attention automaticity bottleneck effect Short-term Memory capacity storage form duration Example 1. Memorize in sequence: 808810844033542 How many right? 15-12 11-8 7-4 4-1 Example 2. Memorize in sequence: 435797100084322 How many right? 15-12 11-8 7-4 4-1 Control Processes in STM Chunking Rehearsal Retrieval Long-Term Memory Capacity Form of Storage Duration Control Processes in LTM Storage Retrieval Are STM and LTM Really Different? Consider: acoustic vs. semantic memories brain injury patients changes due to aging Metacognition/ Executive Control people’s knowledge of their own learning, cognitive processes and their regulation of those processes to enhance learning and memory. Also known as thinking about thinking. Implications for Instruction Encourage multiple representations for encoding Organize information to maximize retrieval Support metacognition Link new material to prior knowledge Minimize interference Recognize STM limitations