* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download PCR Lab Notes
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Short interspersed nuclear elements (SINEs) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genealogical DNA test wikipedia , lookup
Epigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Nutriepigenomics wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Quantitative trait locus wikipedia , lookup
Minimal genome wikipedia , lookup
Biology and consumer behaviour wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid tertiary structure wikipedia , lookup
Transposable element wikipedia , lookup
Extrachromosomal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Human genetic variation wikipedia , lookup
Site-specific recombinase technology wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Population genetics wikipedia , lookup
Genome (book) wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid double helix wikipedia , lookup
Epigenetics of human development wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
History of RNA biology wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
No-SCAR (Scarless Cas9 Assisted Recombineering) Genome Editing wikipedia , lookup
Designer baby wikipedia , lookup
Cell-free fetal DNA wikipedia , lookup
Metagenomics wikipedia , lookup
Human genome wikipedia , lookup
Genome editing wikipedia , lookup
History of genetic engineering wikipedia , lookup
Primary transcript wikipedia , lookup
Hardy–Weinberg principle wikipedia , lookup
Therapeutic gene modulation wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
Helitron (biology) wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Microsatellite wikipedia , lookup
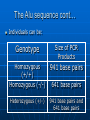
PCR Lab Notes What does PCR Stand For? Polymerase chain reaction Who invented PCR? Kary Mullins Four main areas of biotechnology Gene mapping Cloning DNA sequencing Gene Detection What is the function of PCR? PCR produces exponentially large amounts of a specific piece of DNA from trace amounts of starting material. The steps of PCR 1. 2. 3. Denature the double strand using heat (94 degree Celsius). Anneal Primers – Cool temperature down to 60 degree Celsius. Polymerization – Increase temperature to 74 degree Celsius. Genes and DNA What you already know…. There are 23 pairs of chromosomes which contains 30,000 to 50,000 genes. These genes only comprise about 5 % of chromosomal DNA. The other 95% is non-coding DNA. The sequence with the genes are introns, which is transcribed into RNA but in the end do not make a protein. What you already know cont… The sequence that do code for proteins are called exons. Both introns and exons are initially transcribed, then introns are spliced out of the RNA to create the messenger RNA (mRNA). About the exons and introns Exon sequences are similar among individuals. Introns vary in size and number among individuals. It is the difference in intron sequences that allows us to determine human genetic diversity. The Alu Sequence The Alu sequence is about 300 base pairs long that is repeated, one copy at a time, almost 500,000 times within the human genome. The origin and function of the Alu sequence is not yet known. The Alu sequence cont… Individuals can be: Genotype Size of PCR Products Homozygous (+/+) Homozygous (-/-) 941 base pairs Heterozygous (+/-) 941 base pairs and 641 base pairs 641 base pairs The Hardy-Weinberg Theorem The Hardy-Weinberg equation p2 + 2 pq + q2 = 1 Where: p and q represents alleles. p2 = the expected frequency of the homozygous (+/+) genotype in the population. 2pq = the expected frequency of the heterozygous (+/-) genotype in the population. 2 q = the expected frequency of the homozygous (-/-) genotype in the population. The Hardy-Weinberg equation This equation describes the frequencies of genotypes in a population that is at “genetic equilibrium,” meaning that the frequencies are stable from generation to generation. The Hardy-Weinberg Theory The theory states that for a population to achieve this equilibrium, the population must be: • Very large • The members must mate randomly and produce offspring with equal success • there must be no migration of individuals into or out of the population.