* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 22. Recombinant DNA Technology
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Genome evolution wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression profiling wikipedia , lookup
Agarose gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Comparative genomic hybridization wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
SNP genotyping wikipedia , lookup
Bisulfite sequencing wikipedia , lookup
DNA vaccination wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Transformation (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Restriction enzyme wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
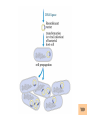
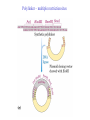
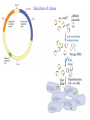
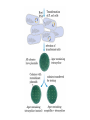
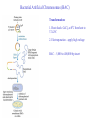
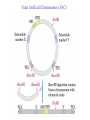
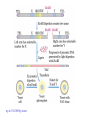
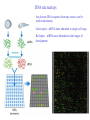
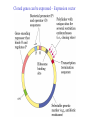
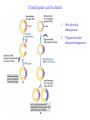
Recombinant DNA Technology Restriction endonucleases - Blunt ends and Sticky ends Restriction endonuclease and DNA ligase yield Recombinant DNA DNA cloning Polylinker – multiple restriction sites Selection of clones Bacterial Artificial Chromosomes (BAC) Transformation: 1. Heat shock: CaCl2 at 0oC then heat to 37-42oC 2. Electroporation – apply high voltage BAC – 5,000 to 400,000 bp insert Yeast Artificial Chromosomes (YAC) up to 150,000 bp insert Studying genes – cDNA library Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) Cloning of PCR products Hybridization allows the deletion of specific sequences DNA fingerprinting – RFLP (restriction fragment length polymorphism) DNA microarrays Any known DNA sequence from any source, can be used in microarray. Green spots – mRNA more abundant in single-cell stage Red spots – mRNA more abundant at later stages of development Cloned genes can be expressed – Expression vector Cloned genes can be altered 1. Site-directed mutagenesis 2. Oligonucleotidedirected mutagenesis Transgenic – cloning in mice for human growth hormone