* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Bacteria and their cell walls
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
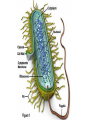
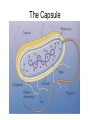
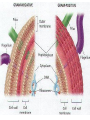
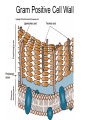
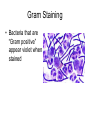
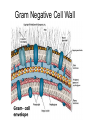
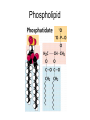
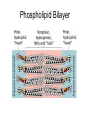
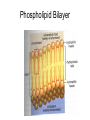
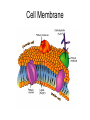
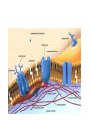
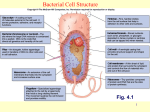
Bacterial Cell Envelope The Pilus Bacterial Cell Envelope • The cell envelope is made up of: – Capsule – Cell wall – Cell membrane • The cell envelope provides the bacteria with: – Structure – Transportation of materials in/out The Capsule The Capsule Made of polysaccharides and protein Protects against dehydration, harmful chemicals, & phagocytosis Attaches bacteria to surfaces Cell Walls • 2 main types of bacterial cell walls: – Gram positive – Gram negative • Named after Christian Gram, a physician who discovered the technique used to differentiate bacteria Cell Walls Gram Positive Cell Wall Gram Positive Cell Wall Gram Staining • Bacteria that are “Gram positive” appear violet when stained Gram Negative Cell Wall Gram Negative Cell Wall Gram Staining • Bacteria that are “Gram negative” appear red Lipopolysaccharides • Only found in Gram negative bacteria cell walls • Provides structure and protection • Considered to be toxic to animals and results in: – Fever – Inflammation – Potentially fatal Positive & Negative Comparison Warm-Up • What are the differences between Gram positive and Gram negative cells? Cell Membrane Phospholipid Phospholipid Bilayer Phospholipid Bilayer Cell Membrane Cell Membrane Transport • Membrane is selectively permeable – Material that normally dissolves in lipids can pass through the membrane – Large particles and charged particles often cannot pass through the membrane – Certain substances (like amino acids) have to pass through special protein passageways