* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Protein_Structure_Final_Powerpoint
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Polyclonal B cell response wikipedia , lookup
Monoclonal antibody wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Butyric acid wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Genomic library wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Homology modeling wikipedia , lookup
Catalytic triad wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
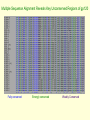
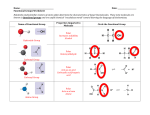
Unconserved Amino Acid Sequences in V3 Domain of gp120 Show No Significant Correlation to Altered Folding and Function Bobak Seddighzadeh Alex George Loyola Marymount University BIOL398-01/S10: Bioinformatics Laboratory March 23, 2010 Outline 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Protein organization determines folding patterns that affect function. Amino acid side chains are in part responsible for protein folding Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where functional changes occur Multiple Sequence alignment reveals unconserved regions of V3 domain Amino acid changes do not affect the structure due to the peripheral location of the V3 loop Scan prosite indicates the function of amino acids are conserved Future studies involving the the conserved regions of the V3 loop as well as other domains can provide better insight Levels of Protein Organization Affect Overall Function • Primary Structure – The number and sequence of amino acids • Secondary Structure – Alpha Helices – Beta-pleated Sheets • Tertiary Structure – 3-D shape of structure • Quaternary Structure – Intra-protein interactions Amino Acid Characteristics Determine Molecular Interactions Classified into Four Types based on R-Group: 1. Uncharged Polar • 2. Nonpolar • 3. Hydrophobic Acidic • 4. Hydrophilic Positive charge Basic • Negative charge * Proline and Glycine are unique Amino Acid Side Chains Play a Large Role in Tertiary and Quaternary Structure 1. Covalent disulfide bonds 2. Electrostatic Interactions 3. Hydrogen bonds 4. Van der Waals forces 5. Hydrophobic Side Chains Mutations in DNA Sequence Can Affect Tertiary Protein Structure • Central Dogma: DNARNAProtein Example: • Sickle Cell Anemia – Single point mutation changes Glutamic acid (hydrophilic) to Valine (hydrophobic) – Results in dysfunctional folding of Hemoglobin A (Tertiary) Determining the Effects of Amino Acid Alterations in Unconserved Sequences • Markham et. al study found that increased diversity and divergence in variants correlated to increased virulence • Kwong et. al study solved the X-Ray structure for gp120 core complexed with CD4 and antibodies • Our question: Will amino acid mutations disrupt the structure of gp120 significantly enough to alter its function? • We hypothesize that specific amino acid mutations in unconserved regions of the V3 loop are responsible for structural change that alters function Rapid and Non-progressors Sequences were Chosen According to High Diversity and Divergence • Rapid Progressors: – Subject 4 • Visit 4 - clones 4,1 • Visit 3 - clones 16,2 • Visit 2 - clones 13, 5 – Subject 10 • Visit 6 - clones 7,4 • Visit 5 - clones 10,3 • Visit 4 - clones 8,5 – Subject 11 • Visit 4 - clones 8,6 • Visit 3 - clones 5,2 • Visit 2 - clones 6,1 • Non Progressors: – Subject 13 • Visit 2 - clones 1,2 • Visit 3 - clones 3,6 • Visit 5 - clones 3,6 – Subject 12 • Visit 5 - clones 6,5 • Visit 4 - clones 2,1 • Visit 3 - clones 3,1 – Subject 2 • Visit 4 - clones 6,5 • Visit 3 - clones 5,4 • Visit 1 - clones 5,1 Multiple Sequence Alignment Reveals Key Unconserved Regions of gp120 Fully conserved Strongly conserved Weakly Conserved More Non-conservative than Conservative Amino Acid Substitutions were Found Between Clones Position 6 10 10 10 10 15 15 20 23 23 23 23 23 23 25 25 39 39 39 43 71 88 88 88 Initial amino acid Final amino acid Serine S13 V5-3 Threonine S2 V3-4 Threonine S11 V4-8,6 Threonine S11 V3-5,2 Threonine S11 V2-6,1 S10 V5-10,3 V6-7,4 Isoleucine Isoleucine S13 V5-6 Leucine S2 V4-3 Serine S10 V5-10 Serine S10 V4-6 Serine S10 V6-7 Serine S12 V3-3,1 Serine S12 V4-2,1 Serine S12 V5-6,5 Glutamic acid S4 V3-16 Glutamic acid S11 V4-8,6, V3-5,2, V2-6,1 Serine S10 V5-10, V4-6,8, V6-4 Serine S10 V5-3 V3-2 Serine S4 V3-16, V2-13, V4-1, Glycine S2 V4-8 Aspargine S12 V5-6 Glutamine S13 V2-1,2 Glutamine S13 V3-3.6 Glutamine S13 V5-3,6 Phenylalanine Methionine Serine Serine Serine Threonine Threonine Proline Alanaine Alanaine Alanaine Threonine Threonine Threonine Glycine Valine Arginine Lysine Lysine Arginine Aspartate Histadine Histadine Histadine Subject Characteristic Change Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Polar Polar to Polar Polar to Polar Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Hydrophobic Hydrophobic to uncharged rigid ring structure Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Hydrophobic Polar to Polar Polar to Polar Polar to Polar Negative charge to Uncharged Negative charge to Hydrophobic Polar to Positive charge Polar to Positive charge Polar to Positive charge Uncharged to Positive charge Polar to Negative charge Polar to positive charge Polar to positive charge Polar to positive charge Kwong et. al. data reveals the peripheral location of the V3 loop gp120 Human antibody CD4 Receptor Gp120 complexes with two antibodies and CD4 receptors Phenylalanine Substitution at Position Six does not Interfere with CD4 Interactions • Needs to be directly touching CD4 • Polar to Hydrophobic change, but located on the surface which does not significantly affect structure Threonine to Serine Substitution at Position Ten has minimal affect on Structure • Serine and Threonine both have hydroxyl's on their side chain making them structurally similar • Residue substitutions on the surface does not affect structure significantly Threonine to Serine is a Polar to Polar Amino Acid Substitution At Position Twenty, the Substitution from Leucine to Proline May Affect the -sheet • The amino acid sequence is buried in the peptide • The direction and nature of the Beta turn can be altered Amino Acid Substitution from Serine to Alanine at Position Twenty-three has Minimal Affect • Serine and Alanine are very similar in size • The residue is located on the surface of the protein -sheet Is Unaffected by Amino Acid Substitution to Glycine at Position Twenty-five • B-pleated Sheets are very forgiving • Glycine is more likely to affect Alpha helices • The residue is located on the surface of the protein Alpha Helices May be Affected by Substituting Glycine to Arginine at Position Forty-three • Lysine to Arginine substitution is small uncharged to bulky positive charge • The residue is located on the surface of the protein structure Scanprosite Analysis Reveals Possible Effects on Glycosylation and Phosphorylation Position 10 Position 23 Position 43 Position 25 Post-Translational Modifications Are Not Affected by Amino Acid Mutations Observed • N-Glycosylation – Typical Sequence = Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr – Important in folding and cell-cell interaction • Phosphorylation – Increases energy so that the protein can undergo subsequent reactions spontaneously – Charged amino acids at the N-terminus affect phosphorylation rate Mutations in Unconserved Regions of the V3 Domain do not Greatly Affect gp120 Function • The structure of the V3 domain remains relatively unaffected by unconserved mutations • The location of the V3 domain may serve as a defense to mutational changes • Glycosylation and Phosphorylation are conserved functions despite amino acid mutations • We reject our hypothesis that amino acid mutations in unconserved regions affect function of the V3 Loop Pancera et al Study Shows Conserved Elements Between gp120 and gp41 May Play Large Role in Viral Entry • Conformational changes in gp120 affect drug and antibody neutralization • The association between gp120 and gp41 plays a role in determining viral cell entry • Defined elements between gp120 and gp41 provides conformational diversity necessary for viral entry Future Studies • Looking into the significance of mutational changes and the rate at which they occur • Analysis of the other domains of gp120 may better suit our investigation References Kwong PD, Wyatt R, Robinson J, Sweet RW, Sodroski J, Hendrickson WAStructure of an HIV gp120 envelope glycoprotein in complex with the CD4 receptor and a neutralizing human antibody Nature v393, p.648-659 Markham RB, Wang WC, Weisstein AE, Wang Z, Munoz A, Templeton A, Margolick J, Vlahov D, Quinn T, Farzadegan H, and Yu XF. Patterns of HIV-1 evolution in individuals with differing rates of CD4 T cell decline. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1998 Oct 13; 95(21) 12568-73. pmid:9770526. Pancera M, Majeed S, Ban YE, Chen L, Huang CC, Kong L, Kwon YD, Stuckey J, Zhou T, Robinson JE, Schief WR, Sodroski J, Wyatt R, Kwong PD Structure of HIV-1 gp120 with gp41-interactive region reveals layered envelope architecture and basis of conformational mobility Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. v107, p.1166-1171