* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download DNA & RNA - East Pennsboro High School
Protein (nutrient) wikipedia , lookup
Promoter (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
RNA polymerase II holoenzyme wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Eukaryotic transcription wikipedia , lookup
Polyadenylation wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Bottromycin wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Protein structure prediction wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Messenger RNA wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Transfer RNA wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
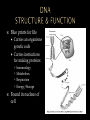
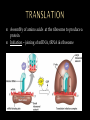
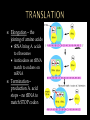
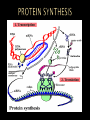
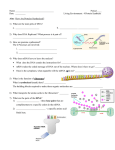
THEIR ROLE IN PROTEIN SYNTHESIS Polymer of nucleotides Deoxyribose (5 carbon sugar) Phosphate group Nitrogen base Adenine Guanine Thymine Cytosine Hydrogen bonds Double helix - two strands twisted Sides – alternating sugar & phosphate grps 5’ end 3’ end phosphate sugar Steps – base pairs Adenine – Thymine Cytosine – Guanine Connected by H-bonds Blue prints for life Carries an organisms genetic code Carries instructions for making proteins: Immunology Metabolism Respiration Energy/Storage Found in nucleus of cell Make a copy of DNA Occur prior to cell division Steps: Enzyme DNA polymerase unzips DNA Two new “complimentary” strands built Single strand Sugar – ribose Phosphate grp Uracil replaces Thymine 3 Types Messenger (mRNA) Ribosomal (rRNA) Transfer (tRNA) Process used to make mRNA from DNA Occurs in nucleus RNA polymerase Enzyme splits DNA so RNA can form Role of mRNA Carries directions making protein to the ribosome Promoter Section DNA where enzyme attaches TATA Box Repeating sequence bases – signals where transcription should begin Immediately followed by start codon AUG CODONS – Groups 3 bases code for an amino acid AUG – “start” codon, codes for methianine 64 different “3-letter” codes for 20 different amino acids Terminator – stop signals UGA, UAA, UAG Assembly of amino acids at the ribosome to produce a protein Initiation – joining of mRNA, tRNA & ribosome Elongation – the joining of amino acids tRNA bring A. acids to ribosomes Anticodons on tRNA match to codons on mRNA Termination – production A. acid stops – no tRNA to match STOP codon DNA TAC GCT AAG ACT MRNA A. ACIDS TRNA Single base is changed – change in 1 a. acid Silent (no change A.Acid) or result in disease Insertion Deletion Addition of base Removal of base Both types result in change of entire amino acid sequence Cytosine insertion on chrom. 16 believed cause Crohn’s disease