* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Theory
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
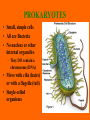
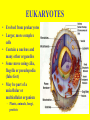
CELL THEORY NOTES THE CELL THEORY -Proposed by Schleiden, Schwann and Virchow -Three parts of the theory: 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. All cells come from other existing cells. CELL SIZE • Why are cells so small? • Small cells have a large surface area to volume ratio • Allows the cell to get all the food and nutrients it needs from its environment – and get rid of the waste it doesn’t need. – The larger the cell gets, the harder this becomes WHAT DO ALL CELLS HAVE IN COMMON? • Cell membrane – Outer boundary of cell, controls what enters and leaves the cell • Cytoplasm (cell interior) – Plasma substance that fills up the ‘space’ around cell organelles • Cytoskeleton (cell skeleton) – Proteins that support cell organelles and keep cell shape • Ribosomes – Found throughout all cells – Sites of protein synthesis PROKARYOTES • Small, simple cells • All are Bacteria • No nucleus or other internal organelles – They DO contain a chromosome (DNA) • Move with cilia (hairs) or with a flagella (tail) • Single-celled organisms EUKARYOTES • Evolved from prokaryotes • Larger, more complex cells • Contain a nucleus and many other organelles • Some move using cilia, flagella or pseudopodia (false feet) • May be part of a unicellular or multicellular organism – Plants, animals, fungi, protists