* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Study guide
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
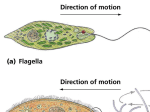
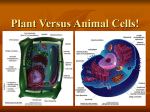
Biology 102, Lectures 8 and 9 Study Guide January 26 and 28, 2004 Brief lecture outline (for more detail, see PowerPoint lecture) I. History of cell study A. Key people B. Cell theory II. Attributes of cells A. Cell size and its limitations B. Cell types III. Cell structures: description and functions A. Structures found in all cells B. Organelles 1. Ribosomes (found in both) 2. Other cell structures (found in eukaryotes) Endoplasmic reticulum Golgi apparatus Lysosomes Flow of membrane within cells Mitochondria Vacuoles Chloroplasts Nucleus C. Cell walls D. Cytoskeleton E. Cilia and flagella Study Questions (2 pages) 1. State the three major principles of the cell theory. 2. Why is there a limit to cell size? Describe two types of problems that would be encountered if cell was significantly larger than they actually are. 3. What four features of cells do all organisms (i.e. both prokaryotes and eukaryotes) contain? 4. What is the major difference between a prokaryote and a eukaryote? 5. What does the cytoplasm include? 6. What feature(s) allow eukaryotes to be much larger than prokaryotes? 7. Be able to describe both the basic structure and the functions of each of the major organelles discussed in class/text. 8. Be able to recognize the particular organelles. 9. Be able to label the key parts of the nucleus and state their function. 10. Describe the flow of membrane within cells, being sure to name the particular structures and the order in which the membrane flows. 11. Be able to name groups of organisms that do, and do not, have cell walls. 12. What is the cytoskeleton? Be able to name the key functions of the cytoskeleton. 13. What are cilia and flagella (in terms of other cell structures). Name some functions of cilia and flagella (i.e. examples from particular organisms). What are the key differences between cilia and flagella?