* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 1 and 10 White
Bird vocalization wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Eyeblink conditioning wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Anatomy of the cerebellum wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Muscle memory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Basal ganglia wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
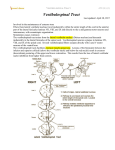
1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. Practice Questions for Neuro Anatomy Lectures 1 and 10 White matter consists of neuronal processes, mainly axons and have connective tissue wrappings like nerves. a. True b. False – no connective wrappings Who thought that the nerves system was a giant synccium of tissue but not made of individual neurons, the reticular theory? a. Camillo Golgi b. Santiago Ramon y Cajal c. Both d. None What is the most common type of neuron? a. Pseduounipolar b. Bipolar c. Multipolar How many purely cranial sensory nerves are there? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 How mane purely cranial motor nerves are there? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 How many mixed cranial nerves are there? a. 2 b. 3 c. 4 d. 5 What motor nerve is trochlear? a. CN 3 b. CN 4 c. CN 6 d. CN 11 e. CN 12 What motor nerve is hypoglossal? a. CN 3 b. CN 4 c. CN 6 d. CN 11 e. CN 12 What motor nerve is abducens? a. CN 3 b. CN 4 c. CN 6 d. CN 11 e. CN 12 10. What motor nerve is oculomotor? a. CN 3 b. CN 4 c. CN 6 d. CN 11 e. CN 12 11. What motor nerve is accessory? a. CN 3 b. CN 4 c. CN 6 d. CN 11 e. CN 12 12. What mixed nerve is vagus? a. CN 5 b. CN 7 c. CN 9 d. CN 10 13. What mixed nerve is facial? a. CN 5 b. CN 7 c. CN 9 d. CN 10 14. What mixed nerve is trigeminal? a. CN 5 b. CN 7 c. CN 9 d. CN 10 15. What mixed nerve is glossopharyngeal? a. CN 5 b. CN 7 c. CN 9 d. CN 10 16. What sensory nerve is vestibulocochlear? a. CN 1 b. CN 2 c. CN 8 17. What sensory nerve is olfactory? a. CN 1 b. CN 2 c. CN 8 18. What sensory nerve is optic? a. CN 1 b. CN 2 c. CN 8 19. If a patient performs an act awkwardly then they likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 20. If a patient performs an act with unexpected and irrelevant movements then they could likely have a: a. Cerebellar lesion b. Cerebral lesion c. Basal ganglia lesion 21. Broadman’s area 4 is the ________ area and is located _______ to the central sulcus and generates neural impulses that control execution of movement. a. Premotor, anterior b. Premotor, posterior c. Primary motor, anterior d. Postmotor, posterior 22. Broadman’s area 6 is the ______ area and is located ______ to area 4 on the lateral and medial surfaces of the frontal lobe. a. Premotor, anterior b. Premotor, posterior c. Primary motor, anterior d. Postmotor, posterior 23. Which of the following controls movements guided by external stimuli? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cortex c. Postmotor cortex d. Supplementary motor area 24. Which of the following is more responsible for planning and learning complex for movements? a. Premotor cortex b. Primary motor cortex c. Postmotor cortex d. Supplementary motor area 25. Axial muscles in the anterior horn are located ______ to those more distal. a. Dorsal b. Ventral c. Medial d. Lateral 26. Flexors in the anterior horn are located ______ to extensors. a. Dorsal b. Ventral c. Medial d. Lateral 27. Other extrapyramidal structures or pathways in addition to corticospinal (or pyramidal) system are involved in control of movement, posture, and muscle tone. a. True b. False 28. This extrapyramidal pathway arises from vestibular nuclei in the pons and medulla and is an important mediator of postural adjustments and head movements: a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 29. This extrapyramidal pathway gives rise to axons that descend ipsilaterally and mediate excitatory influcences upon extensor motor neurons. Brings about postural changes to compensate for tilts and movements of body. What is this pathways? a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 30. This extrapyramidal pathway travels through anterior funiculus to reach cervical motor neurons for neck muscles. It terminates in the cervical region and is important for stabilizing the head during walking and coordinating eye movements and head movements. a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 31. This extrapyramidal pathway arises from reticular formation nuclei in the pons and medulla and descends ipsilaterally and is located in the ventral funiculus. a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 32. This extrapyramidal pathway originates from red nucleus of midbrain and terminate primarily in the lateral parts of the anterior horn influencing distal muscles. It is considered an alternate route for mediation of voluntary movement. a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 33. This extrapyramidal pathway arises from superior colliculus of midbrain and axons pass ventromedially and cross in the dorsal tegmental decussation and in the spinal cord the fibers lie near the ventral median fissure and terminate primarily in cervical segments. a. Reticulospinal pathways b. Vestibulospinal pathways c. Lateral vestibulospinal tract d. Medial vestibulospinal tract e. Rubrospinal pathway f. Tectospinal pathway 34. A patient presents with weakness in extension of his upper arm and flexion of his lower leg, he has no atrophy, has increased resistance to passive stretching of muscles, has hyperreflexia, and has a positive Babinski reflex. Where does this patient likely have damage? a. Upper motor neurons b. Lower motor neurons c. Both 35. A patient presents with flaccid paralysis of individual muscles, atrophy, fasciculation, hypotonia, and hyporeflexia. What does this patient likely have damage? a. Upper motor neurons b. Lower motor neurons c. Both