* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous Tissue
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
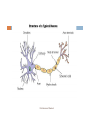
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
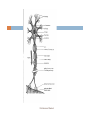
NERVOUS TISSUE Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Nervous Tissue ٢ 1- Central Nervous System (CNS), consists of the brain and spinal cord. 2- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS), consists of cranial nerve, spinal nerves, ganglia, nerve endings and glial cells. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah The Neuron ٣ It is the structural and functional unit of nervous system. It is formed of a nerve cell & its processes (axon & dendrites). Dr.Mohammed Shamiah The nerve cells: ٤ - Size: Range from 4-100 microns. Small cells as in cerebellum. Large cells as in cerebrum. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Structure of nerve cells: ٥ The cell membrane are very thin. The Nucleus has a thick nuclear membrane and clear nucleolus. The cytoplasm contains all cell organoids & inclusions but with no centrioles. The cytoplasm is rich in microtubules & nerofilaments. The cytoplasm is rich in Nissl granules or bodies. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ٦ Nissl granules are specific basophilic bodies consisting of rough endoplasmic reticulum with their attached ribosomes. Nissl granules are not present in axon and near the nuclear or cell membrane. Nissl granules help in nutrition & carrying the memory of nerve cells. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ٧ Mitochondria are present in the body & processes of nerve cell. Cell inclusion of the nerve cells: Glycogen granules are important for the function of the nerve cell. Melanin pigments may be present in some nerve cells. Yellowish lipofuscin granules are present & increase in old age. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Classification of Neurons ٨ According to the shape of nerve cells: I. 1) 2) 3) 4) Unipolar neurons : amacrine cells of the retina. Pseudo-unipolar neurons: spinal ganglia. Bipolar neurons: retina & olfactory mucosa . Multipolar nerve cells: (stellate, pyramidal & pyriform-shaped ) According to the functions: II. 1) 2) 3) Sensory neurons. Motor neurons. Interneurons. According to the length of the axons: III. 1) 2) Golgi Type 1 neurons. (long axons as the neurones of cerebral cortex) Golgi Type 2 neurons. (short axons as neurones of retina) Dr.Mohammed Shamiah NEURON TYPES Bipolar Neuron (retina & olfactory epithelium) Pseudounipolar Neuron (sensory spinal reflex arc) Unipolar Neuron (embryonic) ٩ Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ١٠ Nerve cell processes ١١ The Axon: - Formed of cytoplasm known as axoplasm containing mitochondria, neurofibrils & neurotubule. - Surrounded by membrane called (axolemma). - The Dendrites: They are extensions of the cell body. They conduct nerve impulses towards the cell body. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Differences Between Axon and Dendrites ١٢ The Axon The Dendrites 1. Single process. 2. Thin & long. 3. Uniform diameter along its length. 4. Branches & also give collateral. 1. Usually multiple process. 2. Usually short & thick. 3. Their thickness decreases gradually towards its end. 4. Have many fine side projections called spines. 5. Contains neurofibrils but no Nissl 5. Contain Nissl granules & granules. neurofibrils. 6. Two types of axonal transport 6. Receive impulses from other neurons . exist (Antigrade & retrograde). Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Types of nerve axons according to covering sheath: ١٣ 1- Naked nerve axons without a myelin sheath &without a neurolemma. (e.g. grey matter) 2- Covered with myelin sheath but without neurolemma. (e.g. white matter) 3- Nerve fibres covered with myelin sheath & covered also with neurolemma. (e.g. peripheral somatic axon outside the spinal cord). 4- Covered with neurolemma but are not covered with myelin sheath. (e.g. post ganglionic sympathetic nerve axon). Dr.Mohammed Shamiah The Myelin Sheaths ١٤ It is a fatty tubular covering around the axon. Formed by neurolemma cells surround the peripheral nerves. In the brain formed by neurglia cells(oligodendroglia). Composed of cholesterol, fatty acids &phospholipids. The Myelin Sheaths is white in color. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ١٥ Interrupted at intervals by nodes of Renvier & Lantermann’s clefts. At the nodes of Renvier, the axon not covered by myelin sheath. Lantermann’s clefts: discontinuities in the myelin sheath, facilitate the passage of the nutrition from Schwann cells to the myelin sheath. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Function of Myelin sheath: ١٦ 1) 2) 3) Protection of the axons. Isolates nerve impulses. Accelerate conduction of nerve impulse. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Schwann cells (neurolemmal) ١٧ Formed of chain of Schwann cells around Myelin Sheath. Each cell corresponds to an internodal segment & its comes in contact with axon at the nodes of Ranvier. Function of neurolemmal cells: 1- Isolate nerve impulses. 2- Help in regeneration of neurons. 3- Form the myelin sheath around axons. Dr.Mohammed Shamiah Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ١٨ Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ١٩ Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ٢٠ ANATOMY OF A NEURON axons impulse conduction dendrites axo-somatic synapse axo-dendritic synapse boutons Nissl’s substance axon hillock oligodendrocyte axon myelin sheath myelin sheath myelin sheath axo-axonic synapse unmyelinated collateral central nervous system (CNS) peripheral nervous systen (PNS) Schwann cell motor end plate ٢١ synaptic vesicles motor end Dr.Mohammed Shamiah plate MOTOR NEURON CELL BODY (H&E) DENDRITIC SPINES (boutons)-silver axo-denritic synapses dendrite (boutons) Nissl’s substance nucleolus dendrite nucleus axon ٢٢ Dr.Mohammed Shamiah ٢٣ Thank you Dr.Mohammed Shamiah


















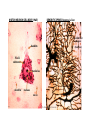













![Neuron [or Nerve Cell]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/000229750_1-5b124d2a0cf6014a7e82bd7195acd798-150x150.png)
