* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download vocabulary - Web Adventures
Selfish brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Subventricular zone wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Node of Ranvier wikipedia , lookup
Multielectrode array wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuroregeneration wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
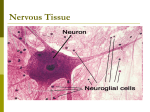
Uncommon Scents Episode Three: Vocabulary VOCABULARY Action potential The electrical signal that is transported along the axons of nerve cells; also called an “impulse”. Adrenaline (uh-DREN-l-in) A body chemical that is released into the blood during stressful situations. It increases the blood pressure by making the heart beat faster. Animal handling regulations Laws and protocols to insure that research animals are provided humane care and treatment. One of the most important federal laws is the Animal Welfare Act by the U.S. Department of Agriculture. Atrophy (A-truh-fee) The partial or complete wasting away of a part of the body. Axon (AK-son) A fiber-like extension from the neuron (nerve) cell body that is used to transport electrical signals from or to the brain. Brain tissue The variety of cells grouped together in the brain. These tissues contain millions of nerve cells (neurons) as well as cells that hold the shape of the neurons, supply nutrition, digest parts of dead neurons, and provide insulation. Burying behavior A mouse’s behavior when confronted with danger; for example, it may bury the source of danger in bedding material. This natural reaction prevents the animal from further contact with the source of danger. Cerebrospinal fluid (suh-ree-broh-SPAHYN-l FLOO-id) A special fluid that surrounds the brain and spinal cord. It protects the brain from damage when the head is shaken or hit. The word is a combination of cerebrum, meaning brain, and spinal, coming from spinal cord. Dendrites (DEN-drahyt) Extensions of the neuron cell body that bring signals from other neurons toward the cell body. Glial cell (GLAHY-uh sel) Brain cells that don’t carry messages. One type of glial cell produces myelin; others provide nutrients or physical support for neurons. 6 Uncommon Scents | Teaching Materials Hypothesis (hahy-POTH-uh-sis) Impulse The electrical signal that is transported along the axons of nerve cells; also called “action potential”. MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) VOCABULARY An educated guess a person makes about a possible outcome. It needs to be testable, and it is always a statement, not a question, because it states what someone thinks or believes will occur. The word origins in the Greek hypotithenai, meaning “to suppose”. A medical imaging technique that visualizes the body’s structure by using a powerful magnets and radio waves instead of X-rays. MRI scans are ultra-clear pictures of a “slice” or section of the body. Multiple Sclerosis (MS) (MUHL-tuh-puh skli-ROH-sis) A disease in which the body destroys the myelin sheath that insulates axons. Without the myelin sheath, the neurons lose their ability to send signals to the muscles. Eventually, this can lead to paralysis. Myelin sheath (MAHY-uh-lin sheeth) A fatty tissue that is produced by specialized brain cells and is wrapped around axons. It insulates the axons and increases the speed in which the neuronal signals are transported. Myelinated (MAHY-uh-luh-ney-tid) Covered with a myelin sheath. Neurons (Nerve cells) (NOOR-on) Cells of the nervous system that specialize in transporting signals from or to the brain or the spinal cord. Neurotransmitters (noor-oh-TRANS-mit-er) Chemical substances that transmits nerve impulses from one neuron (nerve cell) to another. Nucleus A specialized part of a cell that contains the genetic information in the form of DNA. Toluene (TOL-yoo-een) An organic solvent that is used in countless household and industrial products. It usually is liquid, but vaporizes easily and is toxic if inhaled, swallowed, or absorbed. Unmyelinated (un-MAHY-uh-luh-ney-tid) Refers to an axon that is not insulated with myelin. Uncommon Scents | Teaching Materials 7