* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Nervous System - cloudfront.net
Types of artificial neural networks wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Biological neuron model wikipedia , lookup
Axon guidance wikipedia , lookup
Mirror neuron wikipedia , lookup
Endocannabinoid system wikipedia , lookup
Neural oscillation wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Molecular neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Neural coding wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Neuroethology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Microneurography wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Psychoneuroimmunology wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Central pattern generator wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
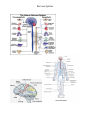
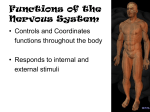
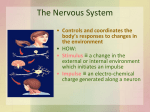
Nervous System Today you will work to identify the function of the nervous system by determining how fast an impulse travels. You will time how long it takes for an impulse to travel though a path. Data Table Trial #1 Trial #2 Time 1: Time 2: Trial #3 Trial #4 Time 3: Time 4: Stand in a circle and hold hands. I will start by squeezing the shoulder of a student. That student will then squeeze their right hand. As soon as each student feels the squeeze on their left hand, they will squeeze the hand to their right. The impulse and timing stops as soon as the impulse reaches the left hand of the student who started the squeeze. Have the student call out when the impulse returns. Record the time for this trial. Encourage students to try to pass the impulse faster on trial #2. Repeat steps. Record data for trial #2. Answer the following. · How could this activity model an impulse? Different types of nerve impulses can travel at different speeds. Regardless of the type, even the top speed is 3 million times slower than the speed of electricity traveling through a wire. Share the following numbers with students: motor impulses travel at 119 m/s sensory impulses travel at 76.2 m/s pain impulses travel at 0.61 m/s Variables will change, because many internal and external stimuli that affect the body. Not all impulses are the same. Repeat the activity in the same manner, but this time instruct students to close their eyes. Nervous System The nervous system is the body’s control center and communication network. The nervous system allows us to think, evaluate, and remember information. The most important part of the nervous system is the neuron or nerve cell. There are three functions of the nervous system: sensory input, integration, and motor input. sensory input– When the eyes see something or hands touch a warm surface, the neurons send a message straight to the brain. This action of getting information from the surrounding environment is called sensory input because things are being sent to the brain by way of the senses. integration– The interpretation, or translation, of things that have been felt, tasted, and touched with the sensory neurons into responses that the body recognizes. This process is accomplished in the brain. motor output– Once your brain has interpreted all that has been sent by using any of the senses, then your brain sends a message through neurons to muscle or other cells, which work to perform the response. Nervous system: The human nervous system is divided into two different systems: the central and the peripheral nervous systems. central nervous system– It is the body’s most rapid means of maintaining homeostasis. The central nervous system regulates vital bodily functions by sensing changes within the body and from the environment. It interprets the changes and makes adjustments in a split second by delivering electrochemical impulses. These impulses result in muscular contractions and/or glandular secretions. The central nervous system consists of the brain and the spinal cord and association neurons. These neurons make up most of the spinal cord and change the input impulse to output impulses and cause the body to respond. peripheral nervous system– There are two types of neurons in this system. — Sensory neurons send information toward the central nervous system from internal and sensory organs. — Motor neurons send impulses away from the central nervous system to voluntary and involuntary muscles. The motor neurons are divided into the somatic nervous system and the autonomic nervous system. interneurons- This is a third type of neuron that sends information between sensory and motor neurons. Answer the following. What organs allow the nervous system to function? What is the function of the nervous system? Nervous System Nervous System