* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Aim: How do substances travel through the cell membrane?
Survey
Document related concepts
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
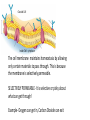
Aim: How do substances travel through the cell membrane? Do Now: Explain how a window screen is similar to cell membrane. Outside Cell Inside Cell- cytoplasm The cell membrane maintains homeostasis by allowing only certain materials to pass through. This is because the membrane is selectively permeable. SELECTIVELY PERMEABLE- It is selective or picky about what can get through! Example- Oxygen can get in, Carbon Dioxide can exit Two Types of Transport Through The Membrane Passive Transport- Substances can move freely through the membrane, no energy needed – No ATP needed Active Transport- Energy Needed to Pass- ATP Required Passive Transport • Diffusion- Movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration without using energy to reach equilibrium to cross the cell membrane. Basically, from where there is more to where there is less. You experience the effects of diffusion when.. someone in your house is baking cookies. You can smell the cookies in your rooms because the molecules from the cookies (greater) are moving across your house (fewer). Particles such as salt and sugars( glucose) pass through the membrane easily. Which direction will these particles move? Some particles can be to large to diffuse through the membrane Osmosis • The diffusion of water across a cell membrane, no energy needed. Hypertonic- more water in the cell If you put this cell in salt water that is 30% salt and only 70% water, which direction will the water travel? Into the cell or out of the cell? Cell: 80% water • It will move from high concentration of water 80% to a lower concentration of water 70%- so OUT of the cell. The Cell will SHRINK Hypotonic- More water out of the cell Which way will water travel? 80% water inside cell 100% water in beaker The water goes into the cell and it bursts!! Isotonic- Same amount of water in and out of the cell Activity: Place the gummy bear into the cup of water, we will check on this cup tomorrow. Make a hypothesis about how you think the gummy bear will look tomorrow. • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=JShwXBWGMyY Exit Ticket Explain the difference between diffusion and osmosis.