* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download 1.3 Cells from Cells
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
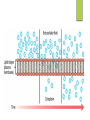
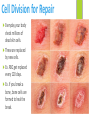
1.3 Cells from Cells Cell from Cells Recall: From the cell theory we established that all cells come from pre existing cells. Cell Reproduction: the process by which new cells are forms. Purpose of Cell Division Allows organisms to do three things: Grow Repair Reproduce Cell Division Cell Division: the process by which a parent cell divides into two daughter cells. What is the importance of cell division? You started as a single fertilized egg now you have trillions of cells. How? Cell division! new cells have constantly been forming as you grow. Cell Division for Growth Every cell faces the problem of needing enough surface area to service its volume. As something gets bigger, the ratio of surface area to volume decreases. When a cell gets too big: Nutrients and water cannot move through it fast enough. Wastes cannot exit fast enough. So then what happens? Cell Division! It must produce smaller cells = more surface area. The Cell Membrane and Diffusion The cell membrane plays a major role in the survival of cells by determining what it allows in and out of cells. For example: when you breathe you take in oxygen and this gets delivered to every cell in your body. How does this access the inside of the cell? Diffusion! The movement of molecules from areas where there are high concentrations to areas where there are low concentrations. Osmosis The diffusion of WATER from an area of high concentration across a membrane. Semipermeable Membrane The cell membrane has a selectively permeable membrane: Some things are allowed in and some things are not Cell Division for Repair Everyday your body sheds millions of dead skin cells. These are replaced by new cells. Ex. RBC get replaced every 120 days. Ex. If you break a bone, bone cells are formed to heal the break. The end … Thank you!! PLEASE FILL OUT THE EXIT PASS 1. STOP 2. START 3. CONTINUE