* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download cell organelle vocabulary quiz
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
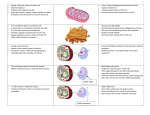
Vocabulary Quiz December 3, 2010 1. Any living thing. Some may exist as a single cell (unicellular) but most are made of many cells (multicellular) such as plants and animals. 2. The part of an organism that is made up of tissues to perform a specific job. Examples of organs include: skin, heart, lungs, stems, leaves, and roots. 3. The basic unit of all living things. 4. The process of matter spreading out evenly from its source. An example is when perfume is sprayed and eventually is smelled throughout a room. 5. All the material between a cell membrane and the nucleus. It includes the various organelles which help a cell to function. 6. The outer portion of a cell. It surrounds the cell and helps keep the contents inside. It also controls what enters or leaves a cell. 7. The outermost part of a plant cell. It is found outside of the cell's membrane. It is quite rigid and helps maintain the shape of the plant. 8. A green structure found inside a plant cell. This structure changes sunlight into a usable form of energy for the plant. 9. The control center of a cell. It contains genetic information that regulates how a cell functions. 10. A special form of diffusion that occurs in liquids. One liquid spreads evenly within another liquid. 11. A group of cells that function together to meet a common purpose. Examples include muscle, bone, and cuticle (the outer covering of a plant). 12. A group of organs that work together performing a common function. Examples of systems include the skeleton, nervous and vascular (tubes in plants). Answers 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. 7. 8. 9. 10. 11. 12. Organism Organ Cell Diffusion Cytoplasm Cell membrane Cell wall Chloroplast Nucleus Osmosis Tissue system