* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
P-type ATPase wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
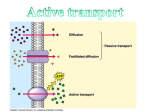
Ch. 4 Cell Membrane Part 3 Active Transport • Definition: • The energy consuming transport of molecules or ions across a membrane AGAINST the concentration gradient • requires cell energy (by hydrolysis of ATP) • Require CARRIER integral proteins • Each carrier protein is specific for just one type of ion or molecule • Examples 1. Sodium–Potassium pump • Exchanges 3 sodium (Na+) ions for 2 potassium (K+) ions 2. Hydrogen ion pump (proton pump) • Pump hydrogen ions against the concentration gradient 3. Endocytosis 4. Exocytosis Importance of Active transport Important is sending signals down axons of nerve cells via Sodium-Potassium pump Important in re-absorption in the kidneys When useful molecules need to be re-absorbed into the blood after filtration into the kidney tubules Important in absorption of some products of digestion Important in plants Used to load sugar from photosynthesizing cells of leaves into the phloem tissue for transport around the plant Used to load inorganic ions from the soil into root hair dermal cells to be transported via the xylem around the plant for metabolism Active Transport Requires ATP (that’s made by cell respiration) ATP adenosine triphosphate ATP attaches to carrier protein in cell membrane PHOSPHORYLATES the carrier protein PHOSPHORYLATION The addition of a phosphate (PO4) group (From ATP) to a protein or a small molecule carrier protein changes shape (conformational change) molecules or ions are transferred across the membrane (against the gradient) Hydrolysis of ATP Protein pumps act as ATPase enzyme Have a receptor site for ATP on the inner membrane Speed up the hydrolysis reaction ATP is hydrolyzed into ADP Energy from hydrolysis is used to change the protein shape Sodium-Potassium Pump Found in membrane of animal cells ROLE: Pumps out 3 Na+ ions and pumps in 2 K+ ions for each ATP molecule Na and K are both cations (positive) Pumping out more Positives than it takes in… Inside of the cell become more negative than the outside Creates a potential difference across the membrane (p.d.) Important in relaying signals in nerve cells Pump runs all the time Uses up 30% of the ATP produced by the cell Nerve cells use up 70% of its ATP running this pump There are separate Na+ and K+ channel proteins that allow ions to diffuse out of cell There are more K+ channel proteins so K+ ions diffuse out of cell more readily/faster than Na+ Types of Transport through Carrier Proteins Active Transport (Uniport) Active Transport Na-K Pump Na-K Pump Antiport Glucose-Sodium Symport Bulk Membrane Transport • Diffusion and active transport refer to then transport of individual molecules and/or ions across membrane • Sometimes large quantities of materials must be transported across the membrane • • • • Large molecules (proteins, polysaccharides) Parts of cells Require lots of energy Bulk transport is a type of ACTIVE transport Bulk Transport: Endocytosis • Endocytosis • Vesicle is created from the infolding of the plasma membrane, which pinches off, bringing large molecules into the cell (forms ENDOCYTIC vacuole) • Pinocytosis – Cell drinking • • • • Bulk uptake of liquids Extremely small vacuoles (vesicles) are formed Sometimes referred to as micropinocytosis Ex. Human egg cell takes up nutrients from cells that surround it (the follicle cells)..called PINOCYTES • Phagocytosis – Cell eating • Cells specializing in this type of transport are called PHAGOCYTES • Forms phagocytic vacuoles • Ex. White blood cells • Receptor Mediated Endocytosis – Substrate binds to receptor found on the plasma membrane to be brought into the cell Ligand – molecule that binds specifically to a receptor site of another molecule LDL uses receptors to enter cells (hypercholesterolemia is due to receptor defect) Bulk Transport: Exocytosis Exocytosis – Vesicle binds to the plasma membrane releasing the contents outside of the cell Reverse of endocytosis Materials removed from cell Secretory vesicles from Golgi apparatus carry proteins to cell surface and release the proteins Ex. Secretion of digestive enzymes from pancreatic cells Ex. Plant cells get their cell wall building materials (cellulose) from secretory vesicle Cells are always trying to Maintain Equilibrium by… 3 ways… PASSIVE Transport 2 types Requires NO energy Goes with Conc. Gradient types: SIMPLE DIFFUSION No protein required Small, uncharged particles FACILITATED DIFFUSION CHANNEL or CARRIER proteins Trans-membrane protein channel Protein with a specific shape; open-close mechanism Ex. Osmosis and ligand-gated channels ACTIVE Transport REQUIRES Energy Goes Against Conc. Gradient ACTIVE TRANSPORT Involves “transporter” membrane protein and ENERGY (ATP) Bulk Transport Endocytosis Pinocytosis phagocytosis Exocytosis