* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5
Survey
Document related concepts
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
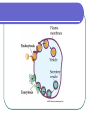
Chapter 5 Section 5.2 Active Transport Active Transport Movement of materials across a cell membrane that requires a cell to expend energy Materials move UP their concentration gradient Cell Membrane Pumps Moves substances up their concentration gradient Moves from an area of lower concentration to an area of higher concentration Sodium-Potassium Pump A special protein that transports Na+ ions and K+ up their concentration gradients To function properly, many animal cells must have a higher concentration of Na+ ions outside the cell and a higher concentration of K+ ions inside the cell Endocytosis Cells ingest external fluid, macromolecules, and large particles (including other cells) Part of the cell forms a pouch around the material then pinches off to form a vesicle Pinocytosis & Phagocytosis Pinocytosis involves the transport of solutes or fluids Phagocytosis involves the movement of large particles or whole cells Exocytosis Vesicles in the cytoplasm fuse with the cell membrane and release their contents out of the cell