* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download reflex
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Single-unit recording wikipedia , lookup
Neuromuscular junction wikipedia , lookup
Embodied cognitive science wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Clinical neurochemistry wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Stimulus (physiology) wikipedia , lookup
Neural engineering wikipedia , lookup
Optogenetics wikipedia , lookup
Caridoid escape reaction wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Sensory substitution wikipedia , lookup
Neuroscience in space wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Channelrhodopsin wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Embodied language processing wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Synaptogenesis wikipedia , lookup
Evoked potential wikipedia , lookup
Circumventricular organs wikipedia , lookup
Development of the nervous system wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
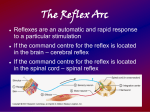
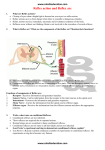
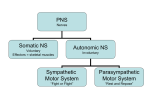
REFLEX ARC A Reflex arc is the neural pathway that mediates a reflex action. In higher animals, most sensory neurons do not pass directly into the brain, but synapse in the spinal cord. This characteristic allows reflex actions to occur relatively quickly by activating spinal motor neurons without the delay of routing signals through the brain, although the brain will receive sensory input while the reflex action occurs. There are two types of Reflex Arc - Autonomic reflex arc affecting inner organs and Somatic reflex arc affecting muscles. When a reflex arc consists of only two neurons in an animal -one sensory neuron, and one motor neuron-, it is defined as Monosynaptic. Monosynaptic refers to the presence of a single chemical synapse. In the case of peripheral muscle reflexes like Patellar reflex, Achilles reflex, brief stimulation to the muscle spindle results in contraction of the agonist or Effector muscle. By contrast, in Polysynaptic reflex pathways, one or more Interneurons connect afferent (sensory) and efferent (motor) signals. All but the most simple reflexes are polysynaptic, allowing processing or inhibition of polysynaptic reflexes within the spinal cord.