* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
History of herbalism wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
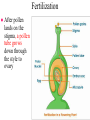
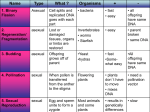
What to do… Take a half sheet of paper. Put your name on the paper. Answer the following question. What is the main function of a lysosome in an animal cell? Breaking down damaged cell parts Plant Reproduction Pieces of Ch. 6 Standard: SPI 4.2 Match flower parts with their reproductive functions Angiosperms (flowering plants) • Plants that protect their seeds within the body of a fruit. • Make up ¾’s of all plants, including: – Trees, shrubs, herbs, grasses, water plants… Structure of a Flower 1. Pistil 2. Stigma 3. Style 4. Ovary 5. Stamen 6. Filament 7. Anther 8. Petal 9. Sepal 10. Receptacle 11. Stem Male Reproductive Structure ❀The stamen consists of two parts: Anther and Filament ❀The anther is where meiosis occurs to produce haploid pollen ❀The filament is a stalk that supports the anther Female Reproductive Structure ❀The pistil consists of the stigma, style and ovary ❀The sticky stigma receives the pollen from the anther ❀The pollen grows a tube down through the style ❀Meiosis occurs in the ovary to produce haploid ovules Reproductive Structures • Petals: colorful structures that attract pollinators. • Sepals: surround and protect the flower bud. Pollination ❀Wind, insects or other animals transfer pollen from the anther of one flower to the stigma of another ❀Flowers vary depending on pollination mechanism Pollination Vectors Wind Pollination: Dull, scentless flowers with reduced petals Bees/Butterfly Pollination: Bright color, nectaries, scent. They sip nectar, get pollen on coats, transfer pollen from flower to flower Bird Pollination: Nectaries, bright colors, tube-like flowers Moth Pollination: White petals, open at night Fly Pollination:Rank odor, flesh colored petals Fertilization ● After pollen lands on the stigma, a pollen tube grows down through the style to ovary Seed and Fruit Development ● After fertilization, the petals and sepals fall off flower ● Ovary “ripens” into a fruit ● The ovule develops into a seed Seed Dispersal MechanismsAllow plants to colonize new areas and avoid shade of parent plant Wind Dispersal - Flight mechanisms like parachutes, wings, etc. Ex. Dandelion, maples, birch Animal Dispersal - Fleshy fruits which animals eat, drop undigested seeds in feces or burrs which stick to animals’ coats Gravity Dispersal - Heavy nuts fall to ground and roll ex. acorns Water Dispersal - Plants near water create floating fruits ex. coconuts Put it together. . . . COLOR and LABEL the following skill sheet on Flower parts. It is homework due TOMORROW if you do not finish in class.