* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download seed dispersal
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Verbascum thapsus wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
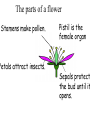
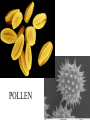
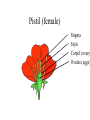
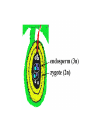
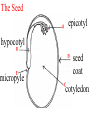
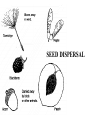
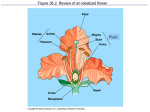
How are new plants formed? • from seeds (sexual reproduction) • by producing things such as bulbs or tubers (asexual reproduction). Structure of a flowering plant There are four main organs of a flowering plant : • The flower - contains the reproductive organs. • The leaves — these use light energy, carbon dioxide and water to make food by photosynthesis. • The stem — this provides support and a transport system for water and minerals to the leaves and flowers and to transport food from the leaves to the roots. • The roots — these anchor the plant to the ground and absorb water and minerals. The Parts of a Flower • Most flowers have four parts: • sepals, • petals, • stamens, • carpels. The parts of a flower Stamens make pollen. Petals attract insects. Pistil is the female organ Sepals protect the bud until it opens. Stamen (male) • Anther: pollen grains grow in the anther. When the grains are fully grown, the anther splits open. stamens POLLEN Pistil (female) • • • • Stigma Style Carpel (ovary Ovules (eggs) stamens pistil Checkpoint 12 Cross pollination pollination is transferred from the male part of one plant to the female part of another plant. Self pollination pollen is transferred from the male part of a plant to the female part of the same plant. BAT POLLINATION BIRD POLLINATORS Wind Pollination These plants typically do NOT have brightly colored flowers. Examples include trees and grasses. Wind Pollination Pollination Regardless of the type, the process is the same. The pollen settles on the stigma, and a pollen tube grows to the ovary. DOUBLE FERTILIZATION (within the ovule) One sperm joins with one egg to form an embryo plant. One sperm joins with two polar cells to become endosperm (stored food). Fruit The ovule turns into the seed and the ovary develops into a fruit. AFTER FERTILIZATION ovule seed ovary fruit The Seed epicotyl hypocotyl micropyle seed coat cotyledon Fruits contain seeds and help to disperse seeds. SEED DISPERSAL dispersal by animals eaten buried stick to fur or clothing WIND DISPERSAL WATER DISPERSAL MECHANICAL DISPERSAL