* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Reproduction
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Fertilisation wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
Pollination wikipedia , lookup
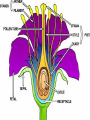
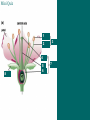
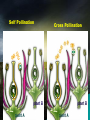
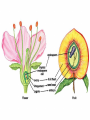
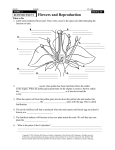
Reproduction Schmit REPRODUCTION AND DEVELOPMENT IN PLANTS Asexual reproduction: - Plants being remade without sex cells (egg or sperm/pollen) Examples of asexual reproduction: A. tip and stem layering – stem comes in contact with ground and develops roots. (Ex. Raspberry bushes) B. cuttings – stem/leaves placed in water; start to develop roots C. Grafting – take a twig from one plant and attach to stem of another D. budding – attach the end bud from one plant and attach it to another E. runners – stems that extend along ground and then “plant themselves” in the ground (ex. Strawberries) F. bulb and corm duplication – onions, daffodils, tulips. Flower is at center. G. Rhizome – horizontal stem growing below ground (ex. Grass) H. Tuber – “eyes” are modified rhizomes that will develop into plants (ex. Potato) SEXUAL REPRODUCTION IN PLANTS Types: Gymnosperms – cone producing Angiosperms – flower producing Monocot One cotyledon Fibrous root Parallel veins Petals in 3’s Dicot two cotyledons tap root branched veins petals in 4’s or 5’s a. Flower parts i. Sepal (all = calyx) Green – leaf like. Protect flower prior to opening ii. Petals (all = corolla) Protect reproductive parts. Attract pollinators iii. Stamen (♂ male parts) 1. pollen contains sperm 2. anther produces pollen 3. filament holds anther up to aid in pollination Pollen iv. Pistil (♀ female parts) 1. stigma pollen sticks to it. 2. style supports stigma aids pollination 3. ovary creates eggs, becomes fruit 4. Ovules – turn into seeds if fertilized 5. Receptacle Point where flower joins stem Variations existing in flowers i. Perfect Both male and female parts ii. Imperfect Male or Female parts Mini Quiz 1 2 3 4 8 5 6 7 pistil c. Pollination a. Pollination – pollen is transferred from an anther to a stigma i. Self-pollination uses own pollen ii. Cross-pollination pollen from a different plant Self Pollination Cross Pollination d. Fertilization = union of egg and sperm i. ii. iii. Pollen lands on stigma pollen tube grows into an ovule sperm is delivered to an egg Pollination Fertilization Pollinators 1. Insects 2. Rain 3. Wind e. Flower Fruit i. ii. ovary ripens into a fruit fruits are filled with seeds MINI QUIZ: Label this flower diagram from memory 2 6 7 3 8 4 9 10 Seeds An embryo plant provided with a food supply and a protective coat Function of Seed Parts testa - protective covering cotyledon – stores food radicle – tip of embryonic root epicotyl – embryonic stem/leaves hypocotyl – embryonic root Hilum – belly button, where egg attached to mom Micropyle – pore where pollen tube connected to egg for sperm entry Germination - The development of a seed into a plant Germination requirements a. water b. oxygen c. temperature Various Methods of Seed Dispersal i. ii. iii. iv. v. Wind, ex. Maple seeds Animal (sticky), ex. burrs Mechanical, pop out, beans Water, coconut Birds, ex. Mulberry Some seeds must pass through a bird or will not germinate What processes must occur? 1. osmosis 2. fertilization 3. germination 4. photosynthesis 5. respiration 6. transpiration 7. growth 8. pollination 9. mitosis 10. meiosis IV. Life Spans of plants a. Annual – only one year i. Ex. Beans, marigolds, etc. b. Biennial – two years, first grow a deep roots, then grow a big top i. Ex. Beet, carrot