* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Name Date ______ Period
Evolutionary history of plants wikipedia , lookup
Plant nutrition wikipedia , lookup
Plant stress measurement wikipedia , lookup
Gartons Agricultural Plant Breeders wikipedia , lookup
Plant use of endophytic fungi in defense wikipedia , lookup
Plant defense against herbivory wikipedia , lookup
History of botany wikipedia , lookup
Ornamental bulbous plant wikipedia , lookup
Plant secondary metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Plant breeding wikipedia , lookup
Ecology of Banksia wikipedia , lookup
Plant physiology wikipedia , lookup
Plant ecology wikipedia , lookup
Plant morphology wikipedia , lookup
Plant evolutionary developmental biology wikipedia , lookup
Perovskia atriplicifolia wikipedia , lookup
Plant reproduction wikipedia , lookup
Flowering plant wikipedia , lookup
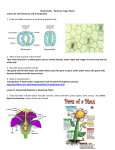
KEY Lesson 9 Reading Questions - The Wonder of Flowering Plants (OMM p. 116119) 1. What type of an organ is a flower to a plant? The reproductive organ 2a.What is the male reproductive structure on a plant? Stamens 2b.What part make up this structure and what do they do? The stamen consists of the anther, which produces the pollen, and the filament, which supports the anther. 3a.What is the female reproductive structure on a plant? Pistil 3b.What part make up this structure and what do they do? The top of the pistil is the sticky stigma, where pollen can attach during pollination, the style supports the stigma and the ovary at the bottom of the pistil produces the eggs. 4. What is the difference between a “perfect” and an “imperfect” flower? A perfect flower contains both male and female reproductive parts, an imperfect flower contains only the male reproductive parts or only the female reproductive parts. 5. What is pollination? When pollen from the anther comes in contact with the sticky stigma of the pistil. 6. What are the two types of pollination and how do they differ? Self-pollination is when the pollen from a plant is transferred to the stigma of the same plant. Cross-pollination occurs when the pollen from a plant is transferred to the stigma of another plant of the same species. 7. How do plants get pollen – explain the method for each type of pollination. In plants that self-pollinate, gravity, an insect, a gust of wind or even a raindrop can help transfer pollen from the anther to the stigma, however in cross pollination the pollen must be transferred to a different plant by wind, water or animals like insects. 8. What is fertilization? When the sperm cells unite with the egg cells fertilization has occurred. 9. How is the endosperm produced? A sperm cell unites with polar nuclei in the egg cell which stimulates the formation of endosperm, which serves as a source of food for the growing embryo. 10. What part of the original flower eventually becomes a fruit? The ovary 11. What is the function of the fruit? The fruit protects the seed and helps in seed dispersal. 12. Why do flowers need to adapt in order to enhance pollination? Because flowers cannot move freely, they must adapt ways to attract pollinators to help them reproduce. The flower’s real function is to promote pollination, fertilization and seed production. 13. How are flowers adapted to encourage pollination? Color and scent attract pollinators to a flower. 14. Draw and label a perfect flower (p. 108). Label the following: petal, sepal, stigma, style, anther, filament, stamen, ovary, stem