* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Macromolecules and Enzymes
Survey
Document related concepts
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Citric acid cycle wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Deoxyribozyme wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Enzyme inhibitor wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Nucleic acid analogue wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Evolution of metal ions in biological systems wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
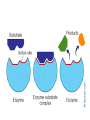
Macromolecules and Enzymes Enzymes • Enzymes – biological catalysts used to speed up reactions • The reaction may still occur without an enzyme present, but it is much slower How do they work? • Substrates – site where the reactants (what is have a reaction) bind to the enzyme • Active Site – site where the substrate binds with the enzyme • The enzyme does NOT change, but the substrate does • The reaction occurs, and the products are released and the enzyme binds with another substrate Effect of temperature and pH • The temperature and pH must be in check for an enzyme to be used • Sometimes that can be too high • Sometimes that can be too low • When the circumstances are too high or too low, nothing happens • When the circumstances are just right, enzymes go to work and the substrates bind Macromolecules • Macromolecules – large organic molecules made from smaller inorganic compounds • There are 4 types: • A. Carbohydrates • B. Lipids • C. Proteins • D. Nucleic Acids Carbohydrates • Carbohydrates – composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen • Includes compounds such as sugars (fructose, sucrose, lactose), glycogen (broken down into glucose), cellulose (found in plant cell walls), and chitin (found in shellfish shells) Lipids • Lipids – made of carbon and hydrogen • This includes fats, oils, steroids and waxes • You also have these as part of the phospholipid bilayer of the cell membrane Proteins • Proteins – compound made of amino acids • Amino Acids – molecules that have a carbon, an amino group, a carboxyl group and another variable group (there are 20 of these and 20 different amino acids) Nucleic Acids • Nucleic Acids – molecules that store and transport genetic information • DNA and RNA