* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch 3 - Fort Bend ISD
Survey
Document related concepts
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
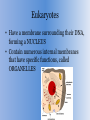
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 3 There are 2 types of cells 1. Prokaryotes 2. Eukaryotes Prokaryotes • Do NOT have a membrane surrounding genetic material, therefore, can make proteins simultaneously when reading genetic code. • Lack some structures found in Eukaryotic cells Eukaryotes • Have a membrane surrounding their DNA, forming a NUCLEUS • Contain numerous internal membranes that have specific functions, called ORGANELLES External Structures – Bacteria • Glycocalyces – Sugar based external surrounding firmly attached to cell’s surface. • Flagella – Tail like structure that propels bacteria (also found on sperm cells). Flow of hydrogen and sodium ions allows movement. • Fimbriae and Pili – Hair like structures that adhere to surfaces to move bacterium. Cell Walls • Found in most prokaryotes – allows attachment to other cells and resistance to antimicrobial drugs. • Eg. Penicillin attacks cell walls of microbes • Peptidoglycan – Polysaccharide, divides cells into two types: 1. Gram-Positive (Thick layer of peptidoglycan) 2. Gram-Negative (Thin layer of peptidoglycan) Cytoplasmic Membrane • Made up of a PHOSPHOLIPID BILAYER: outside is hydrophilic and inside is hydrophobic • Selectively Permeable, but naturally impermeable to large objects • Concentration Gradient – Concentration of sodium ions can attract and repel charged substances into and out of cells. Diffusion • Simple Diffusion - When a small, nonpolar molecule passes through a lipid bilayer. • Channel Diffusion - Channel proteins where material moves through an open, aqueous pore. • Facilitated diffusion - Type of passive transport that is dependent on single transport protein carriers. Osmosis • Movement of water across a selectively permeable membrane driven by a difference in solute concentrations on the two sides of the membrane. Cytoplasm • Gelatinous material inside of a cell • Liquid portion is called CYTOSOL • Contains INCLUSIONS– Deposits of small compounds within the cytoplasm Endospores • Produced by Bacillus and Clostridium • NOT FOR REPRODUCTION • Constitute a defensive strategy for hostile or unfavourable conditions Nonmembranous Organelles • Ribosomes – Sites of protein synthesis • Cytoskeleton – Structure of proteins which gives cells structure and movement: 1. Microfilaments: Fine, thread-like protein fibers, 3-6 nm in diameter 2. Microtubules: Cylindrical tubes, 20-25 nm in diameter 3. Intermediate filaments are about 10 nm diameter and provide tensile strength for the cell. Archaea Glycocalyces • Same characteristics as bacterial glycocalyces Archaea Flagella • Similar to bacterial flagella • About half the thickness (10-14 nm) Fimbriae and Hami • Fimbriae – nonmotile, rodlike, sticky projections • Hami – Fimbria of archaea. Filament frays into 3 hooks. Used for attachment Eukaryotic Glycocalyces • Most animal and protozoan cells lack cell walls • Glycocalyces are anchored through covalent bonds Eukaryotic Cell Walls and Membranes • Cell walls of plants are made of cellulose • Cell walls of fungi are made of chitin or glucomannan • Cell walls of algae are made of cellulose, proteins, agar, carrageenan, silicates, algin, calcium carbonate, or a combination of the aforementioned • ALL have cytoplasmic membrane Centrioles and Centrosome