* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download File
Survey
Document related concepts
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
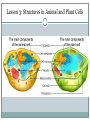
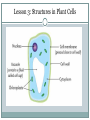
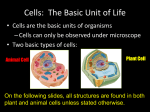
Chapter 1: Cells – the Basic Building Blocks of Life Lesson 3: Comparing plant and animal cells Understand the differences between plant and animal cells Record evidence using a microscope Communicate about cells using scientific terminology Lesson 3: Cells as Building Blocks All living organisms are made of cells – they are the building blocks of life. Cells cannot be seen except under a microscope. This is why it took so long to discover them. Some organisms are made of only one cell; most are made of millions of cells working together. Amoeba is a single-celled organism Lesson 3: Common Structures in Animal and Plant Cells All plant cells and animal cells have three main structures – the nucleus, the cytoplasm and the cell membrane. DNA is inside the nucleus controls reactions and is responsible for cell reproduction Cytoplasm makes up most of the cell and is where chemical reactions happen Small structures inside the cytoplasm called organelles help keep the organism alive Cell membrane surrounds the cell and controls what can get inside (water, oxygen, glucose) and outside the cell (carbon dioxide) Special organelles called mitochondria convert glucose and oxygen into a form of energy that the cell can use. Lesson 3: Structures in Animal and Plant Cells Lesson 3: Differences between Animal and Plant Cells Plant cells also contain: cell wall, vacuole, chloroplasts The cell wall is an extra protective layer outside the cell membrane. It gives the cell shape and strength. The vacuole is a large bubble full of liquid. It provides internal pressure for the cell, keeping it firm and in shape. Leaf cells also contain small, round, green organelles called chloroplasts. These contain a green pigment called chlorophyll, which absorbs energy from the Sun and helps the plant make glucose. Lesson 3: Structures in Plant Cells Lesson 3: Key Vocabulary and Notes Key Vocabulary: nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondria, cell wall, vacuole, chloroplast Key Notes: Animal cells and plant cells contain : nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane, mitochondrion, vacuole Plant cells: also contain, cell wall, chloroplast Chlorophyll allow for plants to make glucose, using energy from sunlight Lesson 3: Questions and Answers 1. Is a cell living? Ans. Yes! 2. Which two parts of the cell are found inside the cytoplasm? Ans. Nucleus, Mitichondria 3. What main substances are allowed through the cell membrane? Ans. Oxygen, glucose, water, carbon dioxide, urea 4. Which two structures give a plant cell its shape? Ans. Cell wall, vacuole 5. Which cell do you think will be larger – a plant cell or an animal cell? Explain your answer. Ans. Plant cell; it has more structures