* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Chapter 5.1 Notes
Survey
Document related concepts
Gene regulatory network wikipedia , lookup
Mechanosensitive channels wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Theories of general anaesthetic action wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Electrophysiology wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
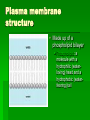
Chapter 5 Membrane Structure and Function part I Page ref. 84-86 Memorize these words!!! inter – within ie. Hilo to Honolulu intra – between, among ie. Hilo to Kona extra – outside of (extracellular would be outside the cell) glyco – containing sugar/carbohydrates (sugar-coated) The fluid-mosaic model of the plasma membrane The cell membrane is a fluid, phospholipid bilayer in which protein molecules are either fully or partially embedded. (see fig. 5.1 and 5.2) Plasma membrane functions to separate the internal from external environment of the cell Regulates materials entering and leaving the cell. Helps the cell, in turn the organism, maintain homeostasis Plasma membrane structure Made up of a phospholipid bilayer Phospholipid: a molecule with a hydrophilic (waterloving) head and a hydrophobic (waterfearing) tail Plasma Membrane Components Cholesterol: a lipid found in bilayer, for strength of membrane Proteins: peripheral (inside surface of membrane) or integral (embedded in membrane) Some integral proteins protrude from one surface of bilayer, some protrude from both (transmembrane) Phospholipids and proteins can have attached carbohydrate (sugar) chains. These are called glycolipids, and glycoproteins, respectively Carbohydrate Chains Carbohydrate chains of proteins in animal cell give cell a “sugar coat” called the glycocalyx. Functions of the glycocalyx include protection of the cell, enables cells to adhere to one another, reception of signal molecules, and for cell-to-cell recognition Fluidity of Plasma Membrane Membrane fluidity critical to it’s functioning At body temperature, it has the consistency of olive oil This allows the cell to do all it needs to do – it makes the cell pliable Homework Due Thursday All vocab AND Reviewing chapter - #1-3 Testing yourself 2,3,11,12,13,14