* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Do Now (Cell membrane Day 1)
Survey
Document related concepts
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
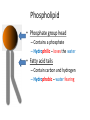
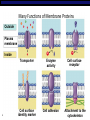
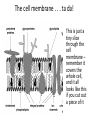
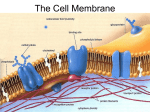
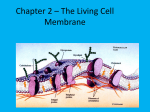
Opening Activity 11/3/15 Scientists refer to the cell membrane as a fluid mosaic model. What is a mosaic? (hint: the pictures below are mosaics) Parts of the cell membrane Essential question: What are the components of a cell membrane, and how do they work? Overview • Cell membrane separates living cell from nonliving surroundings • Controls traffic in & out of the cell – selectively permeable – allows some substances to cross more easily than others Phospholipid • Phosphate group head – Contains a phosphate – Hydrophilic – loves the water • Fatty acid tails – Contain carbon and hydrogen – Hydrophobic – water fearing Phospholipid bilayer • There is water inside and outside the cell • Phospholipids arrange themselves with hydrophobic tails on the inside and hydrophilic heads on the outside. • Together it is the phospholipid bilayer (bi = two) • This is the basic structure of the cell membrane Proteins: channel or transport • Go all the way through the phospholipid bilayer, and have tunnel in the middle • Allow molecules to pass through the tunnel part • May or may not require energy. May or may not change shape as the molecule goes through. Many Functions of Membrane Proteins Outside Plasma membrane Inside AP Biology Transporter Enzyme activity Cell surface receptor Cell surface identity marker Cell adhesion Attachment to the cytoskeleton The cell membrane . . . ta da! This is just a tiny slice through the cell membrane – remember it covers the whole cell, and it all looks like this if you cut out a piece of it Cells Video • http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=dPKvHrD1 eS4 9 Finish Build-A-Membrane • Make sure your name is on your model and put it in the bin at the front of the room • Put the worksheet in the In-Box at the back of the room • Clean up & put away all supplies 10 Closing Activity/Exit Ticket You will turn this in! Give Me 5! •On a ½ sheet of paper with your name, date, and period, write down 5 words that come to mind when you think about the structure of the cell membrane (individual words, not a sentence)