* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Biochem Option (D)
Maurice Wilkins wikipedia , lookup
Protein adsorption wikipedia , lookup
Cell-penetrating peptide wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding RNA wikipedia , lookup
Transcriptional regulation wikipedia , lookup
Community fingerprinting wikipedia , lookup
Molecular cloning wikipedia , lookup
Gel electrophoresis of nucleic acids wikipedia , lookup
Non-coding DNA wikipedia , lookup
Silencer (genetics) wikipedia , lookup
Epitranscriptome wikipedia , lookup
Vectors in gene therapy wikipedia , lookup
Expanded genetic code wikipedia , lookup
DNA supercoil wikipedia , lookup
Proteolysis wikipedia , lookup
Gene expression wikipedia , lookup
Cre-Lox recombination wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Molecular evolution wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
List of types of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Artificial gene synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Biochemistry wikipedia , lookup
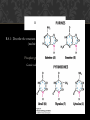
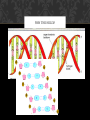
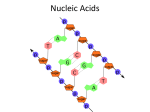
BIOCHEM OPTION (B) B1 Calculate the energy value of a food from enthalpy of combustion data. Key ideas: Q = m*c*ΔT c = specific heat of a substance (4.18 J/g̊ C) * = the substance CHANGING Temp. Assumption Q lost = Q gained SAMPLE PROBLEM 1.00 g of cereal raises the temperature of 400. cm3 of water in an insulated food calorimeter from 23.7̊C to 33.4̊C. Calculate the energy value per gram of the cereal, assuming the heat capacity of a calorimeter is negligible and given the specific heat of water = 4.18 J/g ̊C. WARM-UP 1/5 1. Draw the general formula of 2-amino acids 2. Describe the characteristic properties of 2-amino acids Zwitterions- m.p., b.p., solubility in water Amphoteric B.2.3 Describe the condensation reaction of 2-amino acids to form polypeptides When do they become “proteins”? B.2.4 Describe and explain the primary, secondary, tertiary and quaternary structure of proteins B.2.5 Explain how protein can be analyzed by chromatography and electrophoresis B.2.6 List the major function of proteins in the body Structural Biological Catalysts Hormones Antibodies Transport Energy* HOMEWORK B3-carbohydrates and B4-lipids Tomorrow B8 Nucleic Acids B8 NUCLEIC ACIDS B.8.1: Describe the structure of nucleotides and their condensation polymers (nucleic acids or polynucleotides): Phosphate group, pentose sugar, nitrogen base Genetic code = it’s all about the nitrogen bases! B.8.1 Distinguish between structures of DNA and RNA DNA = thymine, RNA = uracil DNA = deoxyribose RNA = ribose CONDENSATION REACTION Forms nucleoside (nitrogen base and pentose sugar) then complete nucleotide (with the phosphate group) • Acidity/basicity of nucleotide and component parts? • Charges? NUCLEIC ACID Polymer of nucleotides Enzyme catalyzed condensation reaction B.8.3 Explain the double helical structure of DNA • Secondary structure • Why do Adenine and Thymine only pair with each other (and Cytosine and Guanine)? WHY THE HELIX? B.8.4 Describe the role of DNA as the repository of genetic information and explain its role in protein synthesis. • What is a gene? • How does the DNA in your cells compare with one another? With other organisms of the same species? Different Species? Offspring? • What might happen if a part of a gene is damaged? PROTEIN SYNTHESIS DNA mRNA (transcription) mRNA polypeptide chain (translation with tRNA) Why is it three nucleotides to make a codon = 1 amino acid? B.8.5 OUTLINE THE STEPS INVOLVED IN DNA PROFILING AND STATE ITS USE https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZxWXCT9wVoI&list=PLxvLFTHItXp Q1khokrwlQvVPZckHxRwCn https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Fz6p8EgJZ3w