* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Activities
Survey
Document related concepts
Mechanical calculator wikipedia , lookup
Ethnomathematics wikipedia , lookup
Infinitesimal wikipedia , lookup
Georg Cantor's first set theory article wikipedia , lookup
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Positional notation wikipedia , lookup
Bernoulli number wikipedia , lookup
Hyperreal number wikipedia , lookup
Large numbers wikipedia , lookup
Real number wikipedia , lookup
Elementary arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Location arithmetic wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
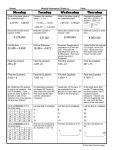
Maths Weekly Plan: Summer 1st wk 1 12/4/10 Main teaching Objectives Day 1 Day 2 Day 3 Add several small numbers. Write numbers 3–9 twice each on the board. Chn write an addition using 5 of the numbers, and find the answer. Roll 2 dice to create a 2-digit number, if possible between 21 and 51. Whose addition came to this answer? Check. Repeat several times. All Y5 Write 9+16=. Easy way to add 9? 16+10–1=25. Add near multiples What’s special about 9, 16, 25? Square of 10 and 100 to 2numbers. (Draw square grids to demo.) Show and 3-digit that 9+16=25 can be written as 3²+4²=5². Is it numbers always true that adding 2 consecutive square Partition numbers nos gives the next square no.? Explore. into H, T and U, Add several multiples of 10. Write on board: 30+50+80+10+80. Remind chn to look for pairs making 100, or doubles. Chn work out answer and write on whiteboard, waiting for signal before holding it up. Check answers. Write a new addition of multiples of 10. Continue like this. All Remind chn of rounding method. We can use it to add near multiples of 100. Write 298+428. Write 300+428=728. We added 2, so must subtract 2 (726). Write 46+38+149+62. Pairs rewrite ready for chosen method: ordering, rounding and splitting. Discuss. [ITR Y5 D2.c] Count on or back in steps of 0·1 to/from 5. Say and write a starting number, eg 1·0, one point zero. Go round the class, each child adding on 0·1 until you reach 5. Choose child to give new start number from 1 to 5. Rpt the process but this time count backwards to 0. All Choose Y6 chn to write a sequence of square numbers from 1² up to 15². This is a sequence. Write a sequence of decimals in steps of 0·5: 2·0, 2·5, 3·0, 3·5, … Look at the pattern. Rpt for steps of 0·2 and 0·25. Focus on patterns created by sequences. Y5 Point to 9+16=25. We can use a rounding method to add near multiples of 10. Write 69+347, 69 is very close to 70. Write 70+347=417 Remind chn to subtract 1 (416). Pairs choose either partitioning or rounding method to calculate149+286. Demo both. Which do you prefer? Y6 Write 72=. On calculator demo finding answer, eg 7×7, 7××. Rpt for 92, 202, 3002. Chn make square numbers table for multiples of 10. Use to estimate 162 then find on calculator (256). Demo checking using inverse operation: 256. Compare to estimates. [ITR Y6 D2.c] Y5 Write 4·5+1·8=. Draw 4–7 number line marked in tenths. Child marks 4·5. Show how add 0·5 to get next whole number, then add remaining 1·3 making 6·3. Write 3·5+4·3. This time the tenths = less than 1 unit, so easier to add by splitting units and tenths (7·8). [ITR Y5 D2.d] Activities Group 1 Group 2 Group 3 Group 4 [group] [TB] [TB] [pair] Y5 D2.c.1 Adding 99 to a series of 3-digit numbers Y5 5.2 p59 Adding 3-digit numbers using near multiples Y6 6.2 p58 Writing square numbers and finding next square after a given number Y6 D2.c.1 Writing square numbers and exploring their digital roots [TB] [TB] adding the most significant digit first Y6 Know squares of numbers to at least 12 × 12 Derive squares of multiples of 10 Calculate squares of larger numbers Check with the inverse operation when using a calculator Develop calculator skills and use a calculator effectively Begin to find a number that has a given square, i.e. its square root Y5 Mentally add or subtract a pair of decimal numbers, crossing units or tenths Use known number facts and place value for mental addition and subtraction of decimals [group] [TB] Y5 5.2 p58 Y5 5.2 p61 Adding near Exploring multiples to 3- general digit numbers statements about adding Y6 D2.c.2 Finding square numbers, and the differences between adjacent squares Y6 6.2 p60 Finding squares of large numbers [group] [TB] [group] Y6 6.2 p59 Finding squares of multiples of 10 and 100 Y6 D2.c.3 Estimating and calculating square roots of non-square numbers [TB] Y5 D2.d.1 Y5 5.2 p63 Adding 1-place Adding two 1decimals to place decimal make the next numbers whole number Plenary Outcomes Choose a pair of chn to think of an addition that could be done using the rounding method. Ask rest of class to say an answer. Check and repeat, choosing different chn to generate an addition. Y5 Add near multiples of 10 and 100 Y6 Know squares of numbers to at least 12×12 Use number Y5 cards 11–99. Partition, adding Choose child to most significant pick a card, eg digit first 32. Pairs estimate Add near its square, then multiples of 10 use calculator to and 100 find it. Compare Y6 with estimates. Calculate Who was squares and closest? square roots Check using inverse operation Ask chn to work Y5 in pairs. Pairs Add 1-place generate and decimals, write a pair of 1crossing units or place decimal tenths numbers that total Y6 a whole number. Calculate Allow a minute or squares and two then check square roots their numbers. Abacus Evolve Mixed-Age Planning Year 5 and 6 Weekly Plan © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 Mental oral starter Block D2.c: Y5 Add near multiples of 10; Y6 Recognise square numbers Block D2.d: Y5 Add and subtract decimal numbers; Y6 Explore number sequences Day 4 Recognise and name different quadrilaterals. Play ‘Shape pointing’. Chn each have a shape board (Y6 PCM 208). Give Show me instructions based on properties of quadrilaterals, eg Show me a parallelogram. Chn point at shape. Rpt. Extend to eg Show me a kite in third row. Day 5 Estimate acute, obtuse & reflex angles. Prepare some angles, incl. acute, obtuse and reflex. Show them. Point at one. Chn estimate its size in degrees. They record and reveal their responses on whiteboards. Discuss. Measure with a protractor. Who was closest? Rpt. Vocabulary add added addition square numbers triangular numbers consecutive rounding method subtract partition multiples of 10 multiples of 100 ordering splitting calculator estimate Main teaching Objectives Activities Group 1 Y5 (Continued) [WCT] All Count in 2s starting at 2. Chn repeat the count, Find what to add Y5 D2.d.2 only saying the units digits. Focus on the pattern to a decimal to Exploring created by the sequence. Repeat for the multiples make the next patterns in of 3, 4, 5, … 10. Make lists to compare the whole number digital roots patterns. Y6 Y5 Write 3·8+1·6=. Draw p-v grid. Split numbers into Recognise and extend number units and tenths and rewrite addition: sequences 3+1+0·8+0·6=4+1·4=5·4. Write 3·8–1·6=. Model Count on or back using the same method (partitioning) to do in steps of 0·1, subtraction. First subtract units (3–1=2); then 0·2, 0·25, 0·5… subtract tenths (0·8–0·6=0·2), so 3·8–1·6=2·2. Explore patterns [TB] All created by Write £3·64+£2·75=. Discuss how to add them. Y5 5.2 p62 number Partition into £s, 10ps and 1ps. Rewrite addition Adding to find sequences on p-v grid, splitting numbers into units, 10ths and the difference Recognise and between two 2100ths. Chn work in 3s to complete the 3 explain patterns additions and combine to find total. Use same place decimal and method to subtract, eg £5·79–£2·36. numbers relationships, Y6 generalise and Stick Post-it note on board. How many? (1) Stick predict 2 more below. How many? (3) Stick 3 more. How Begin to many? (6) These are triangular numbers. Chn recognise predict next few nos and write sequence. Add 2 triangular consecutive triangle nos. What do you notice? numbers Answers = square numbers. [ITR Y6 D2.d] inverse operation sequence pattern decimals units tenths hundredths next whole number £ 10p 1p doubles count on count back triangle quadrilateral Plenary Group 2 Y5 Group 3 Y6 Group 4 Y6 [WCT] [pair] [TB] Y5 D2.d.2 Exploring patterns in digital roots Y6 D2.d.1 Exploring patterns in Pascal’s triangle Y6 6.2 p63 Writing next number in harder sequences [group] [TB] [pair T] Y5 D2.d.3 Y6 6.2 p62 Adding to make Writing the next whole numbers to number continue sequences parallelogram angles acute obtuse reflex Y6 D2.d.2 Generating and exploring Fibonacci’s sequence Outcomes Write Y5 4·2+9·3+3·8=. Add 1-place Ask some pairs to decimals split the numbers Subtract 1-place into units and decimals, tenths, and look crossing units or for pairs of tenths tenths that make a unit. Y6 Agree answer. Explore patterns created by number sequences What is sum of Y5 first 10 counting Add 1-place numbers decimals (1+2+3+4 Add/subtract …+10)? The sum amounts of is the 10th money, crossing triangular units or tenths number. Write Y6 first 10 triangular Explore number numbers: 1, 3, 6, sequence ... 55. Sum of Recognise numbers 1–10 = triangular 55. Rpt for first 15 numbers counting numbers. Resources 2 dice cubes individual whiteboards calculators Y6 PCM 159b number cards 0-99 shape board Y6 PCM 160a Bingo boards protractor Post-it notes Y5 PCM 151a circles with 0-9 marked around circumference (Y5 PCM 238) Blocks D2.c and D2.d Abacus Evolve Mixed-Age Planning Year 5 and 6 Weekly Plan © Pearson Education Ltd 2008 Mental oral starter