* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Ch on Drugs and Prep for Test
Affective neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
Proprioception wikipedia , lookup
Brain morphometry wikipedia , lookup
Neurophilosophy wikipedia , lookup
Human multitasking wikipedia , lookup
Neurolinguistics wikipedia , lookup
Haemodynamic response wikipedia , lookup
Nervous system network models wikipedia , lookup
Biology of depression wikipedia , lookup
Activity-dependent plasticity wikipedia , lookup
Limbic system wikipedia , lookup
Cortical cooling wikipedia , lookup
Premovement neuronal activity wikipedia , lookup
Emotional lateralization wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience wikipedia , lookup
History of neuroimaging wikipedia , lookup
Environmental enrichment wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychology wikipedia , lookup
Synaptic gating wikipedia , lookup
Feature detection (nervous system) wikipedia , lookup
Metastability in the brain wikipedia , lookup
Holonomic brain theory wikipedia , lookup
Neuroplasticity wikipedia , lookup
Neuroesthetics wikipedia , lookup
Cognitive neuroscience of music wikipedia , lookup
Human brain wikipedia , lookup
Brain Rules wikipedia , lookup
Neural correlates of consciousness wikipedia , lookup
Neuroeconomics wikipedia , lookup
Aging brain wikipedia , lookup
Time perception wikipedia , lookup
Neuroanatomy wikipedia , lookup
Neuropsychopharmacology wikipedia , lookup
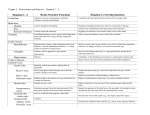
* * Depressant * Act out * Reckless behavior * Lessons our inhibitions by turning off our frontal lobe * Most widely used drug, 90% * Can lead to dependency * Once removed, headaches and drowsiness * Stimulant * Speeds up the functioning of the brain * Derived from opium * Natural substance * Why they wreak havoc * Produce drowsiness * Insensitivity to pain * Eliminates pain and anxiety * Duplicating Endorphins * * From the leaves of the Coca plant * Euphoric sense of happiness and increased activity * Stimulant * Powerful * Prevents the terminal buttons from reabsorbing dopamine * Works as an anesthetic * * Intensifies sensory experiences * Attach to receptors that are related to long term memory * Amotivational syndrome * Coupled with well established barriers to learning, pot smoking can cause people to waste a lot of time and money * Brain development is affected * * Research shows that marijuana aids some medical conditions * Chemotherapy problems – decreases vomiting, nausea, and anxiety * Aids – improves appetite * Pain and muscle spasms – decreases these plus depression * Glaucoma – decreases pressure on eye * * Hallucinogens, similar to mushrooms * Intensification of sensations and experiences * Dream like state * Mescaline, better known as peyote, is derived from a Chihuahan cactus found in Texas and Mexico * It has been used medicinally and sacramental for thousands of years * US government allows its use in Native * American religions * Comes from cactus buttons * * Dopamine is released * Pleasure follows * This nudges us into eating, drinking, and other beneficial behaviors * Years of research has revealed that ingesting many drugs also causes dopamine to be released * The dopamine circuit begins in the ventral tegmental area * synthesizes dopamine which it passes to the * Nucleus accumbens which then connects through its axons to areas of the frontal lobes * Continued use of some drugs (opiates) causes neurons to shrink or otherwise work less effectively, forcing the user to rely on the drug for pleasure. * * Stage 1 –brain is slowing down * Stage 2 – 4 waves slow gradually and become increasingly rhythmic, indicating less activity, eyes still inactive * After Stage 4, we move back through Stages 3 and then 2, but instead of then going into Stage 1, we enter into …. * REM sleep in which our eyes suddenly move about, as if we were awake, and our brain waves become fast and choppy like Stage 1 * These cycles run for about 90 minutes * * Occipital lobe * Located in the lower back region of the head * Contains many specialized areas relating to different aspects of vision, especially the primary visual center * Many links to the temporal for visual tasks * Parietal * Primarily devoted to the sense of touch * Contains the primary somatosensory cortex * Area within it is taken up by the parts of the skin * Also tells us where we are in space relative to the objects around us * * Frontal * Its back region contains the primary motor cortex which takes information from the primary somatosensory cortex and then moves the body’s muscles * Similarly, the parts of the body with more sophisticated muscle systems have more space in the primary motor cortex devoted to them * Temporal * Contains the primary auditory cortex * Much of it is used for complex visual tasks in conjunction with the primary visual cortex * These include recognizing faces and perceiving motion * Also crucial to memory * In the left hemisphere, aids language skills * * Central Nervous System * Autonomic Nervous System * Sympathetic Nervous system * Parasympathetic Nervous System * MRI * Basic Types of Neurons * Corpus Callosom * Left brain equals language * Brain Structure * Hindbrain * Hippocampus * Amygdala *