* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Choosing Healthful Foods
Ribosomally synthesized and post-translationally modified peptides wikipedia , lookup
Peptide synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
Ancestral sequence reconstruction wikipedia , lookup
Expression vector wikipedia , lookup
Magnesium transporter wikipedia , lookup
Fatty acid metabolism wikipedia , lookup
Point mutation wikipedia , lookup
Interactome wikipedia , lookup
Metalloprotein wikipedia , lookup
Basal metabolic rate wikipedia , lookup
Protein purification wikipedia , lookup
Western blot wikipedia , lookup
Nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy of proteins wikipedia , lookup
Protein–protein interaction wikipedia , lookup
Two-hybrid screening wikipedia , lookup
Genetic code wikipedia , lookup
Biosynthesis wikipedia , lookup
Amino acid synthesis wikipedia , lookup
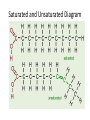
Choosing Healthful Foods Lesson 25 Proteins • Two Kinds of Proteins: complete protein and incomplete protein • Complete Protein: contains all 9 of the essential amino acids • Incomplete Protein: protein from plant sources outside of soybeans that don’t contain all 9 essential amino acids What to know about proteins continued…. • Amino Acids: acids that bond together to make a strand of protein • You need 20 amino acids for your body to function properly. The body makes 11 of those amino acids. The 9 you need from food are known as essential amino acids. • Example of complete protein: meat, fish, poultry, milk, yogurt, and eggs • Example of incomplete protein: grains, legumes, nuts, seeds Amino Acids • histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine are the essential amino acids meaning you need to receive them in your diet. • The ones that your body makes are as follows: arginine (conditionally essential only if your body doesn’t make it), alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, cysteine, glutamic acid, glutamine, glycine, proline, serine and tyrosine. Carbohydrates • Two Kinds of Proteins: Simple and Complex • Simple: sugars that enter the bloodstream rapidly to provide quick energy (glucose) • Complex: sugars that enter the bloodstream slowly and are stored for future use (fiber/starches) • Complex Carbohydrates are broken down into simple sugars by digestive enzymes and saliva • Examples of Simple: table sugar • Example of Complex: grains, potatoes Fiber • Part of the vegetable that can’t be digested. • Two types of fiber: soluble and insoluble • Soluble fiber: binds with cholesterol in the bloodstream to prevent it from building up in artery walls creating heart attacks and heart disease. • Insoluable fiber: binds with water to help produce bowel movements reducing colon cancer. • Examples: wheat pasta (insoluble), apple skin (soluble) Fats • Main job is to help body utilize vitamins that are taken in via food or by choice. Also, source of energy and helps heat body. • Two types of fat: Saturated and Unsaturated • Saturated fats are hard for the body to break down because they have stronger bonds. Saturated fats become solid if left at room temperature. • Example: Fat around meat and dairy products • Unsaturated fats are easier for the body to break down because their chemical make up allow them to bond with other molecules to create a chemical reaction. • Example: Olive Oil, Peanut Oil, Fish Oil Saturated and Unsaturated Diagram Vitamins/Minerals Vitamins: a nutrient that helps the body use carbs, proteins, & fats. • Two Types of Vitamins Fat Soluble and Water Soluble. • Fat Soluble: A, D, E,&K health benefits on page 286. • Water Soluble: C, & B health benefits on page 286. Minerals: a nutrient that helps regulate chemical reactions in the body • Two types: Macro and Trace Minerals. Macro= >100mg example-sodium and calcium. Trace examples iron and zinc. Health Benefits on page 287. Proper Portion • Five Food Groups: Protein, Vegetable, Fruit, Dairy, and Grains. • Protein: 14-18 Boys-6.5 oz. Girls-5 oz. • Dairy: 14-18 Boys/Girls-3cups • Grains: 14-18 Boys/Girls -6 oz. ½ whole grains • Vegetables: 14-18 Boys-8 oz. Girls 2.5 oz. • Fruit: 14-18 Boys-16 oz. Girls- 12 oz. • www.choosemyplate.gov Eating Disorders • Eating Disorder- the condition in which a person is compelled to stave, to binge, or to binge/purge. • Anorexia-the ability to eat as little as possible creating starvation • Bulimia-the ability to eat and purge afterwards to not gain weight from food consumption.