* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Diffusion
Survey
Document related concepts
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell membrane wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
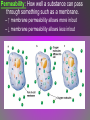
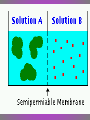
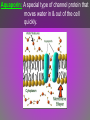
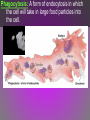
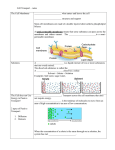
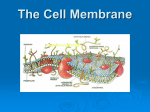
Diffusion: Movement of particles from an area of high concentration to low concentration. – Concentration & permeability are the factors that determine if diffusion occurs across a membrane or not. Concentration: The amount of dissolved solute (substance) in a volume of solvent (liquid). – Solution = solvent + solute – If a substance is present in unequal amounts on either side of a membrane, it will move to the area of lower concentration until equilibrium is reached. Permeability: How well a substance can pass through something such as a membrane. – ↑ membrane permeability allows more in/out – ↓ membrane permeability allows less in/out PASSIVE TRANSPORT • Passive transport: Movement of materials in or out of the cell which does NOT require use of cell energy (ATP). – Cells live in a liquid environment which makes it easier for materials (food, water, gases) to move in & out of the cell. – 2 types: Osmosis & facilitated diffusion Vorticella Osmosis: Diffusion of H2O molecules through a semi-permeable membrane from an area of ↑ H2O concentration to ↓ H2O concentration. – 3 types of solutions (hypertonic, isotonic, hypotonic) Osmotic pressure: The force exerted by osmosis, that moves water across a semi-permeable membrane from a diluted solution to a more concentrated solution. – Occurs in hypotonic, isotonic, & hypotonic solutions Hypertonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where solute concentration is higher than the concentration inside the cell. H2O leaves cell; Cell shrinks. – ↑ solute in solution, ↓ solute in cell – Plasmolysis: The shrinking of the cytoplasm due to the loss of H2O. Isotonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where the solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside the cell. H2O enters/ exits cell at an even rate. Cell doesn’t shrink or expand. Ideal conditions. – solute in solution ↔ solute out of cell Hypotonic solution: An osmotic solution (outside cell) where the solute concentration is lower than the solute concentration inside the cell. H2O enters cell; Cell expands. – ↓ solute in solution, ↑ solute in cell – Cytolysis: The bursting of a cell. HYPOTONIC ISOTONIC HYPERTONIC FACILITATED DIFFUSION Facilitated diffusion: The transport of materials across the plasma membrane by means of transport proteins. 1. Channel proteins 2. Carrier proteins Channel Protein: Tube-like proteins in the cell membrane through which small, dissolved particles can diffuse. Aquaporin: A special type of channel protein that moves water in & out of the cell quickly. Carrier proteins: A protein in the cell membrane whose shape fits a specific molecule or ion. – When the proper molecule binds with the protein, the protein changes shape and moves the molecule across the membrane. ACTIVE TRANSPORT Active transport: The movement of materials against the concentration gradient. – Molecules move from ↓ concentration to ↑ concentration • Chemical energy (ATP) from the cell is used to change the shape of a protein to move molecules across the cell membrane. ENDOCYTOSIS Endocytosis: A process in which a cell surrounds & takes in material from its environment. – A vacuole is then produced and taken into the cell. endocytosis Phagocytosis: A form of endocytosis in which the cell will take in large food particles into the cell. Pinocytosis: A form of endocytosis in which the cell takes liquids into the cell. EXOCYTOSIS Exocytosis: A process in which the cell removes large particles or wastes exocytosis