* Your assessment is very important for improving the workof artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Cell Transport Quiz KEY
Survey
Document related concepts
Model lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
Lipid bilayer wikipedia , lookup
Cytoplasmic streaming wikipedia , lookup
SNARE (protein) wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Membrane potential wikipedia , lookup
Organ-on-a-chip wikipedia , lookup
Ethanol-induced non-lamellar phases in phospholipids wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Signal transduction wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Transcript
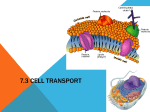
Name Block Cell Transport Quiz KEY Directions: Write the correct word for each definition. Each word should only be used once. Osmosis Hypertonic Isotonic Phospholipid Receptor Active transport Fluid mosaic model Passive transport Diffusion Concentration gradient Phagocytosis Hypotonic Facilitated diffusion Endocytosis Selective permeability Exocytosis 1. Equal solute concentrations in two solutions. 2. Difference in the concentration of a substance from one location to another. 3. Protein that detects a signal molecule and performs an action in response. 4. Molecule that forms a double-layered cell membrane. 5. Movement of molecules from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. 6. Solution that has a higher solute concentration compared to another solution. 7. Movement of molecules across a membrane from low to high concentration; requires energy. 8. Release of substances out of a cell by the fusion of a vesicle with the membrane. 9. Solution that has a lower solute concentration compared to another solution. 10. Diffusion of water molecules across a membrane from high water concentration to low water concentration. 11. Diffusion of molecules assisted by protein channels that pierce a cell membrane. 12. Used by cells to take in large materials or liquids, the cell membrane folds in and forms a vesicle. isotonic 13. Allowing some substances, but not others, to cross the membrane. 14. Movement of molecules across the cell membrane without energy input from the cell (high to low concentration). 15. Model that describes the arrangement and movement of the molecules (lipids, proteins, cholesterol) that make up a cell membrane. Selective permeability Concentration gradient receptor phospholipid diffusion hypertonic Active transport exocytosis hypotonic osmosis Facilitated diffusion endocytosis Passive transport Fluid mosaic model 16. Used by cells to take in large solid particle, the cell membrane “grows” out around the particle. phagocytosis Directions: Label the diagram with the following terms: Phospholipid, hydrophobic region, hydrophilic region, integral protein, cholesterol